20 MicroBlaze Development Kit Spartan-3E 1600 Edition User Guide
www.xilinx.com UG257 (v1.1) December 5, 2007
Chapter 3: Clock Sources
R
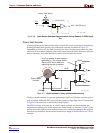
Clock Connections
Each of the clock inputs connect directly to a global buffer input in I/O Bank 0, along the
top of the FPGA. As shown in Table 3-1, each of the clock inputs also optimally connects to
an associated DCM.
Voltage Control
The voltage for all I/O pins in FPGA I/O Bank 0 is controlled by jumper JP9.
Consequently, these clock resources are also controlled by jumper JP9. By default, JP9 is set
for 3.3V. The on-board oscillator is a 3.3V device and might not perform as expected when
jumper JP9 is set for 2.5V.
50 MHz On-Board Oscillator
The board includes a 50 MHz oscillator with a 40% to 60% output duty cycle. The oscillator
is accurate to
±2500 Hz or ±50 ppm.
Auxiliary Clock Oscillator Socket
The provided 8-pin socket accepts clock oscillators that fit the 8-pin DIP footprint. Use this
socket if the FPGA application requires a frequency other than 50 MHz. This socket is
populated with a 66 MHz oscillator. This clock input is used for some of the reference
designs provided with the board. Alternatively, use the FPGA’s Digital Clock Manager
(DCM) to generate or synthesize other frequencies from the on-board 50 MHz oscillator.
SMA Clock Input or Output Connector
To provide a clock from an external source, connect the input clock signal to the SMA
connector. The FPGA can also generate a single-ended clock output or other high-speed
signal on the SMA clock connector for an external device.
UCF Constraints
The clock input sources require two different types of constraints. The location constraints
define the I/O pin assignments and I/O standards. The period constraints define the clock
period—and consequently the clock frequency—and the duty cycle of the incoming clock
signal.
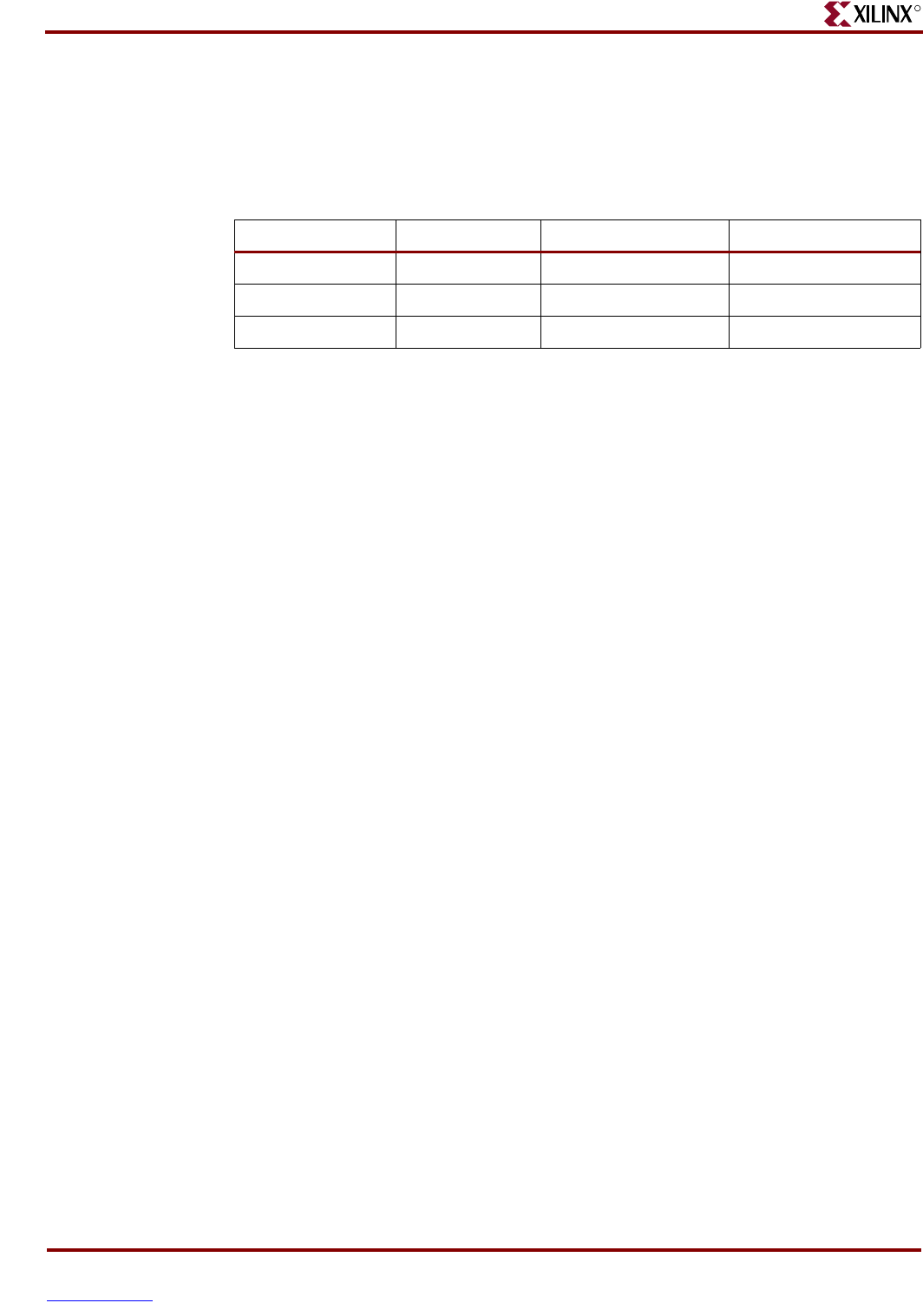
Table 3- 1: Clock Inputs and Associated Global Buffers and DCMs
Clock Input FPGA Pin Global Buffer Associated DCM
CLK_50MHZ C9 GCLK10 DCM_X0Y1
CLK_AUX B8 GCLK8 DCM_X0Y1
CLK_SMA A10 GCLK7 DCM_X1Y1