What is a network? 97
as Class C. The next 21 bits identify the network and the last 8 represent the local
or host address, limiting the number of devices to 256. In contrast, a Class A
network allocates 24 bits for local addresses, allowing for many more devices.
IP addresses are composed of four sets of eight bits usually separated by a period
(for example, 192.168.1.1).
The IP address of the 56K LAN Modem identifies the 56K LAN Modem itself and
the network it creates when devices are connected to the Ethernet ports.
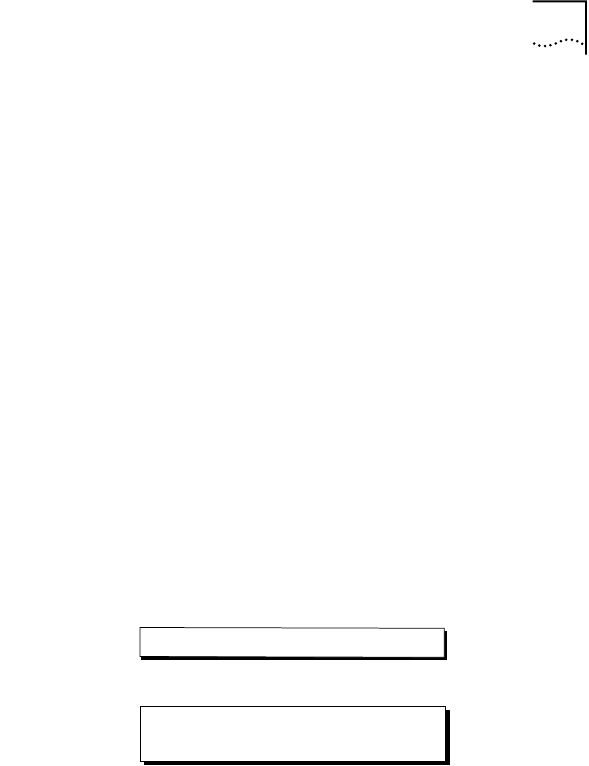
What is a Subnet Mask? Many networks are divided further into smaller sub networks. A subnet mask is a
number that identifies the sub network to which your computer is connected. The
subnet mask differentiates the part of the IP address that represents the network
and the part that represents the host.
The bits of the subnet mask are set to 1 if the host should treat the corresponding
bit in the IP address as part of the original network number. These bits in the mask
are set to 0 if the host should treat the bits as part of the device number as shown
in Figure 46.
Figure 46 Subnet Mask
Dynamic and Static IP
Addresses
IP addresses for public networks must be unique and provided by the Network
Information Center (NIC). Because of the increasing popularity of the Internet, the
NIC is running out of permanent IP addresses. It is therefore becoming more
common to use dynamic IP addresses, which are assigned temporarily and then
reused, instead of static IP addresses which are permanently assigned. For
example, when accessing the Internet, your ISP has a pool of IP addresses it uses to
provide temporary connections to multiple users. Once you disconnect from the
Internet, the IP address you were using is placed back in the pool for use by
another user.
If your LAN will not connect to the public Internet, you can set up your own
unique (that is, private) IP address numbering. IP addresses for private networks
such as an office LAN must also be unique but only within that LAN.
What is DHCP? Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is a process that automatically assigns a
unique, temporary IP address to a newly attached computer on an IP network.
What is DNS? Domain Name Service translates the common alphabetic name into the numeric IP
address. For example, www.3com.com is translated to an specific IP address by
DNS. If you do not use the DHCP functionality of the 56K LAN Modem, you will
have to manually configure the following parameters for each computer on the
LAN: IP address, subnet mask, DNS address and default gateway.
IP Address Network Number Device Number
Subnet Mask 11111111 11111111 11111111 00000000
Subnet Address Network Number Subnet Device
Number


















