53
When the unit is operating in CV mode, the CV Control Voltage varies between - 0.5Vdc and + 0.5Vdc. It is most negative
when the load is drawing no power but as power output increases the voltage becomes more positive.
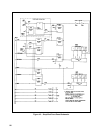
Protection Subsystem
The diverse system configurations and operating environments under which the unit will be required to operate, will
certainly require it to be adequately protected if it must function reliably. The protection circuits of the unit offer protection
at turn-on and also during operation.
The CURRENT LIMIT RESISTORS is the first protection along the power rail which the unit utilizes. This circuit
prevents any surges of AC input to the input filter by limiting the inrush current. After a predetermined elapsed time the
resistor is bypassed and the unit is ready to deliver power. The circuit which carries out this function is the TIMED DELAY
CIRCUIT. When both the Dropout Detector and the
PCLR are high, this delay circuit is enabled and counting at the clock
frequency of 1.25KHz begins. After 3 seconds,
DROPOUT goes high and enables the PWM.
Turn-on protection is also offered by the BIAS VOLTAGE DETECTOR (BVD) which prevents spurious operation that
may occur at power-on of the unit if circuits attempt to operate before the + 5Vdc bias voltage is at the clock, PWM, and
logic circuits. After power-on, as the output of the + 5Vdc bias power supply rises the BVD is turned on inhibiting the
Relay Driver and the On-Pulse Driver and creating the power clear signal
PCLR . The latter signal is held low until the
unregulated input to the + 5Vdc bias supply is greater than an input voltage sufficient to assure a + 5Vdc output
Certain circuits also give the unit on-going protection during its operation The AC SURGE AND DROPOUT DETECTOR
is such a circuit. This circuit protects the unit from damage from AC mains voltage surges. It shuts down the unit when
there is either a 40% overvoltage or a 20 ms voltage interruption in the ac mains voltage. The mains detect signal senses the
ac mains voltage and pulls the DROPOUT signal low thereby inhibiting the PWM and shutting off the power.
During conditions of overvoltage when a monitored fraction of the output voltage exceeds the limit set by the front panel
OVP Adjust, the OVER VOLTAGE PROTECTION circuit inhibits the PWM and triggers the Down Programmer. This
condition persists until the unit is turned off. At power-on, the Bias Voltage Detector resets the OVP.
The DOWN PROGRAMMER is another protection circuit which is activated when any of the following adverse operating
conditions occurs: over voltage; over temperature; primary power failure; and programming of a lower output voltage.
Under these conditions, the Down Programmer lowers the output voltage by rapidly discharging the output filter capacitors.
The Down Programmer takes its input from the Master Enable and the CV Error Amplifier. When either of these signals is
low, it is activated. The + 8.9Vdc bias supply provide enough energy to the Down Programmer to discharge the output
circuit even when primary power is lost.
The TEMPERATURE PROTECTION circuit protects the FETs from excessive temperature gradients. A thermostat
mounted on the FET heat sink monitors the temperature build up of the FETs and disables the PWM when the temperature
exceeds a predetermined limit.
In addition to an over-temperature protection, there is also an OVERVOLTAGE PROTECTION circuit. When the FETs
turn off, the leakage inductance of the power transformer forces current to continue to flow in the primary. Clamp diodes
are employed to protect the FETs from excessive reverse voltage by bypassing the FETs and conducting the current to the
input filter.
Input Power Subsystem
This subsystem forms the interface between the ac mains supply and the switching elements of the unit. It takes ac power
from the mains, converts it to dc and delivers this unregulated dc to the switching elements and internal control circuitry.
Input power takes two distinct pathways to carry out the above function: mains -rectifier/filter--switching elements and
mains--bias supply--control circuits.