Chapter 3 Thermal Design of Platforms Using the AMD Processor-In-a-
Box (PIB) Thermal Solution
19
Thermal Design Guide for Socket F (1207) Processors
32800 Rev. 3.00 August 2006
Note: Do not cut entirely through the center rib. Doing so will compromise the stiffness of the
backplate.
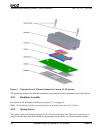
The plate uses two PennEngineering (PEM) standoffs that serve multiple purposes. The PEM
standoffs serve as attachment points for the retention frame screws. They also align the backplate
properly to the motherboard. Features in the retention frame slide over the standoffs and allow the
installation of the screws with a minimum chance of cross threading. Additionally, four M3.5 PEM
standoffs in the backplate serve as attachment points for the socket.
The insulator prevents the backplate from electrically shorting to the motherboard. A pressure-
sensitive adhesive in the insulator keeps the backplate in place against the motherboard during
assembly. The insulator also is thick enough to prevent any significant capacitive coupling between
the motherboard and backplate.
3.3.2 Retention Frame
The plastic retention frame, made of 20% glass-filled Lexan, is a two-piece implementation rather
than the single-piece frame used for socket 940. This change accommodates the larger foot-print of
socket F (1207) processors.
The retention frame serves multiple purposes. The retention frame aligns the heat sink and provides a
stop for the heat sink in large shock-force events. The retention frame and backplate are attached to
the motherboard by the motherboard vendor. Two screws securely hold the backplate and retention
frame together. The two mounting tabs on the retention frame serve as attachment points for the heat
sink spring clip.