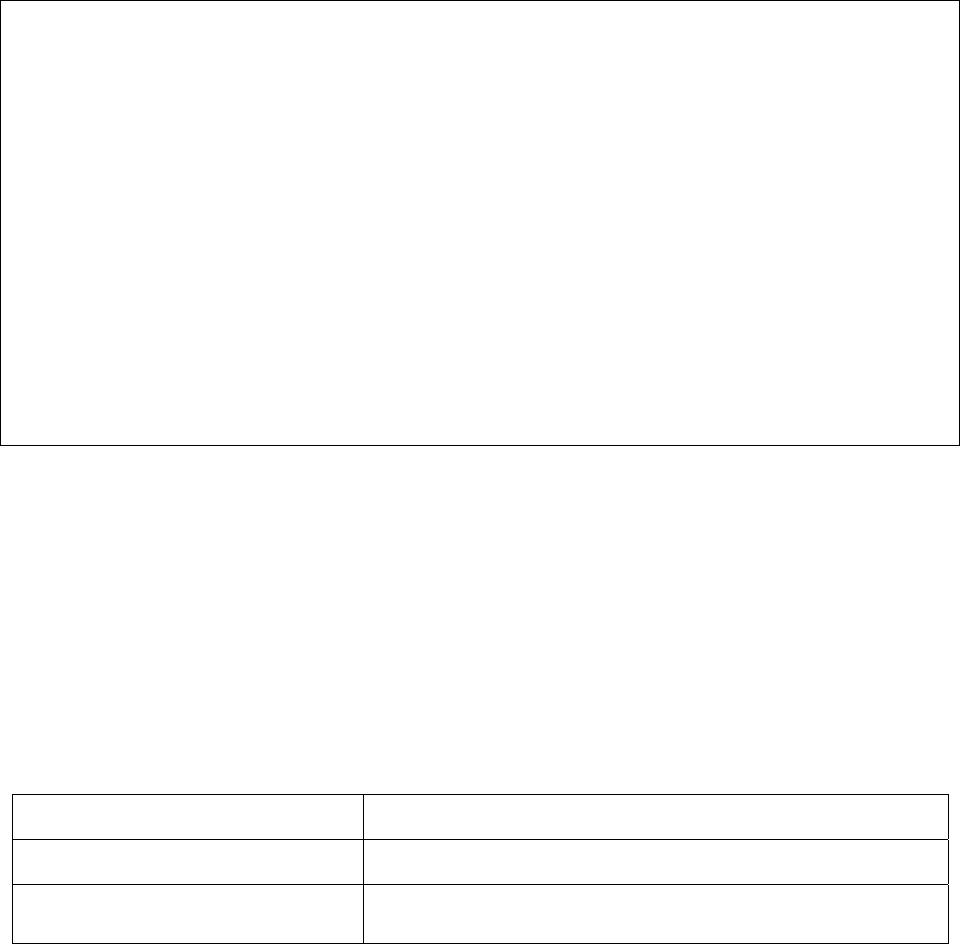
In general, the top (privileged) commands allow you to change terminal settings on a temporary basis, perform basic
tests, and list system information. To list the commands available in top mode, enter a question mark (?) at the
prompt, as shown in the following example. Enter a question mark (?) after a command to see all the options for that
command.
Switch> enable
Switch# ?
clear Reset functions
clock Manage the system clock
configure Enter configuration mode
copy Copy from one file to another
debug Debugging functions
disable Turn off privileged mode command
erase Erase a filesystem
exit Exit current mode and down to previous mode
help Description of the interactive help system
ip Global IP configuration subcommands
no Negate a command or set its defaults
ping Send echo messages
quit Exit current mode and down to previous mode
reload Halt and perform a cold restart
show Show running system information
snmp-server SNMP related functions
write Write running configuration to memory, network, or terminal
cls Clear screen
Important: To retain configuration changes after a system reload you must save changes made in running
configuration to the startup configuration file. From the privileged level, configurations can be saved using the write
command or by using the copy running-config startup-config command.
4.3 Global Configuration Mode
Global configuration commands apply to features that affect the system as a whole, rather than just one protocol or
interface. Commands to enable a particular routing function are also global configuration commands. To enter the
global configuration mode, use the configure command.
The following example shows how to access and exit global configuration mode and list global configuration
commands.
Command Purpose
Switch# configure
From privileged EXEC mode, enters global configuration mode.
Switch(config)# ?
Lists the global configuration commands.
26 Asante IntraCore IC36240 User’s Manual


















