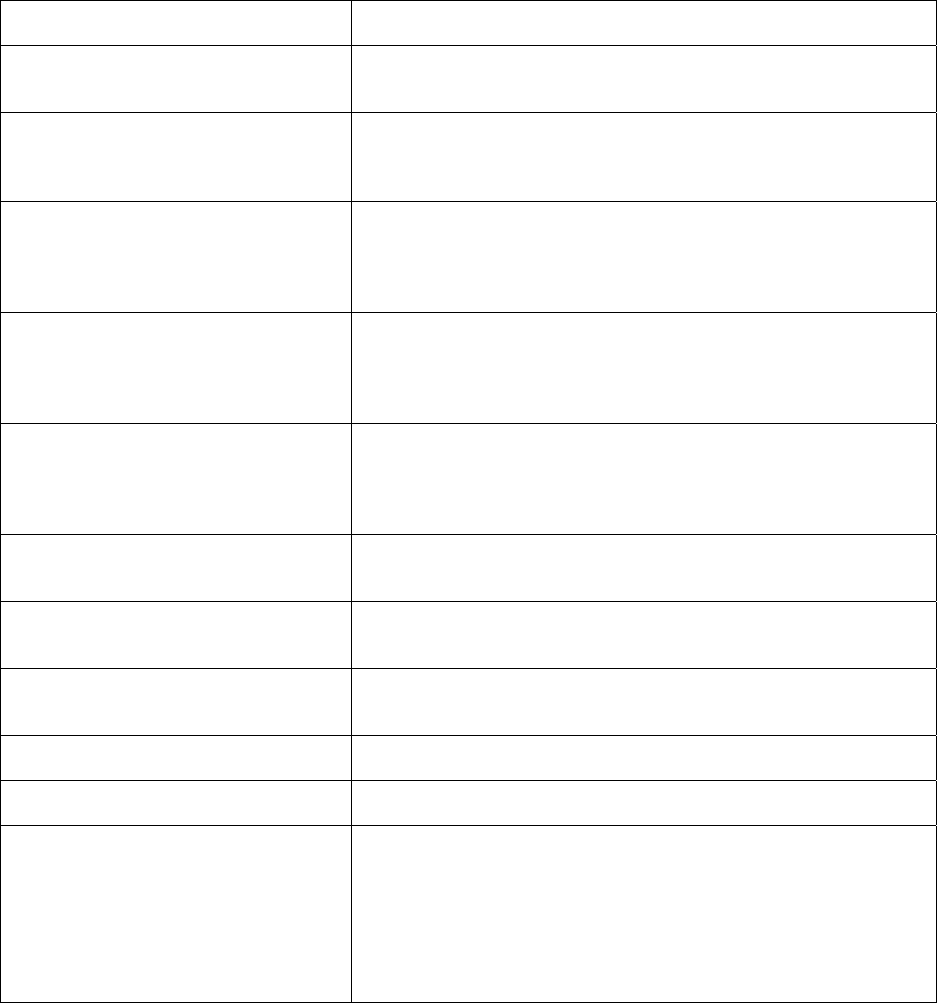
5.3.5 SNMP Configuration Commands
Command Purpose
snmp-server
Enable the SNMP agent. The first snmp-server global configuration
command enables SNMP.
snmp-server engineID {local engineid-
string|remote host-ip-address [udp-port
port-number] engineid-string}
Set Engine ID for local or remote devices. The remote engine ID is
used to create users that can send SNMPv3 traps.
snmp-server view view-name subtree
[subtree-mask] [included | excluded]
Define the SNMP server view. Currently, the SNMP subtree can only
adopt numbered form. That is, “1.3.6.1.2.1” is valid but “mib-2” is
invalid. The subtree-mask uses colon-separated hex digits, such as
“FF:A0”.
snmp-server group group-name {v1 |
v2c | v3 [auth | noauth ]} [read
read-view] [write write-view] [notify
notify-view] [access access-list]
Set SNMP views. The default read-view is “all,” and the default write-
view and notify-view are “none”.
snmp-server user user-name group-
name [remote host-ip-address [udp-
port port-number]] { v3 [auth {md5}
auth-password]}
Define SNMP server users. (Currently creating “v1|v2” users and the
“sha”(SHA1) algorithm are not supported)
snmp-server enable traps [ duplicate-
ip |snmp | station-move]
Enable SNMP traps. Supported trap types are authentication,
duplicate-ip, and station-move.
snmp-server trap-timeout seconds
Define how often to resend trap messages. The range is 1–1000. The
default is 30 seconds.
snmp-server queue-length length
Set the message queue length for each trap-host. The range is 1–
1000. The default is 10.
snmp-server contact text
Set the system contact string.
snmp-server location text
Set the system location string.
show snmp
show snmp engineID [local | remote]
show snmp groups
show snmp user
Show various SNMP information.
5.4 Configuring Spanning Tree
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is part of the IEEE 802.1D standard. It provides for a redundant network without
the redundant traffic through closed paths. For example, in a network with redundant path but without spanning tree
protocol, the same message is broadcast through multiple paths, leading to an unending packet-passing cycle. This
in turn causes a great amount of extra network traffic, leading to network downtime. The STP reduces a network
traffic, with multiple, redundant connections, to one in which all points are connected, but where there is only one
path between any two points (the connections span the entire network, and the paths are branched).
46 Asante IntraCore IC36240 User’s Manual


















