2-6
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Running the Setup Wizard
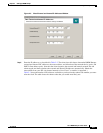
Table 2-2 Enter External and Internal IP Addresses Field Descriptions
Field Description
External Network ID Enter the external network IP address block assigned by your ISP. The number
after the slash is the subnet code for the number of IP addresses available in the
block.
Default Gateway This IP address is automatically generated based on the external network ID
that you entered. You cannot change the first three sets of numbers in this
address. This IP address is the address of the gateway (router) assigned by the
ISP and used to access the Internet. Here’s what can and cannot be changed in
this field:
• You cannot change the first three sets of numbers in the IP address.
• The fourth set defaults to the number 1. You can change this fourth octet
after the Setup Wizard populates the Default Gateway based on the
External Network ID.
Your router needs to be configured for the internal network to point to the
external NIC of the BBSM Hotspot server. If you are using a private IP address,
you will also need to create a network address translation (NAT) pool for end
users and one-to-one NAT statements for remote access to internal network
devices.
Internal Network ID This is the Network ID for the subnet that end users use to connect to the BBSM
Hotspot network and, through it, the Internet. The internal subnet consists of the
network devices, end-user clients (such as laptops and PDAs), and the BBSM
Hotspot internal NIC. The number after the slash is the subnet code for the
number of IP addresses available in the block.
You can enter your own private network ID, or you can input a public network
ID.
Primary DNS Server Enter the IP address for the primary domain name system (DNS) server
provided by your ISP. Because BBSM Hotspot is not configured as a DNS
server, DNS forwarding is enabled to forward all DNS requests to a remote
DNS server. BBSM Hotspot acts as a DNS forwarder for end-user DNS requests
as well as its own DNS requests. These requests, such as www.cisco.com, are
resolved into IP addresses so the Internet routers can locate the web server with
the content.
Table 2-3 Subnet Code Conversions
Subnet Code
Number of
IP Addresses
/29 6
/28 14
/27 30
/26 62
/25 126
/24 254