1.5:
Power
Quality
Q
Power quality can mean several different things. The terms "power quality" and "power quality
problem" have been applied to all types of conditions. A simple definition of "power quality
problem" is any voltage, current or frequency deviation that results in mis-operation or failure of
customer equipment or systems. The causes of power quality problems vary widely and may
originate in the customer equipment, in an adjacent customer facility or with the utility.
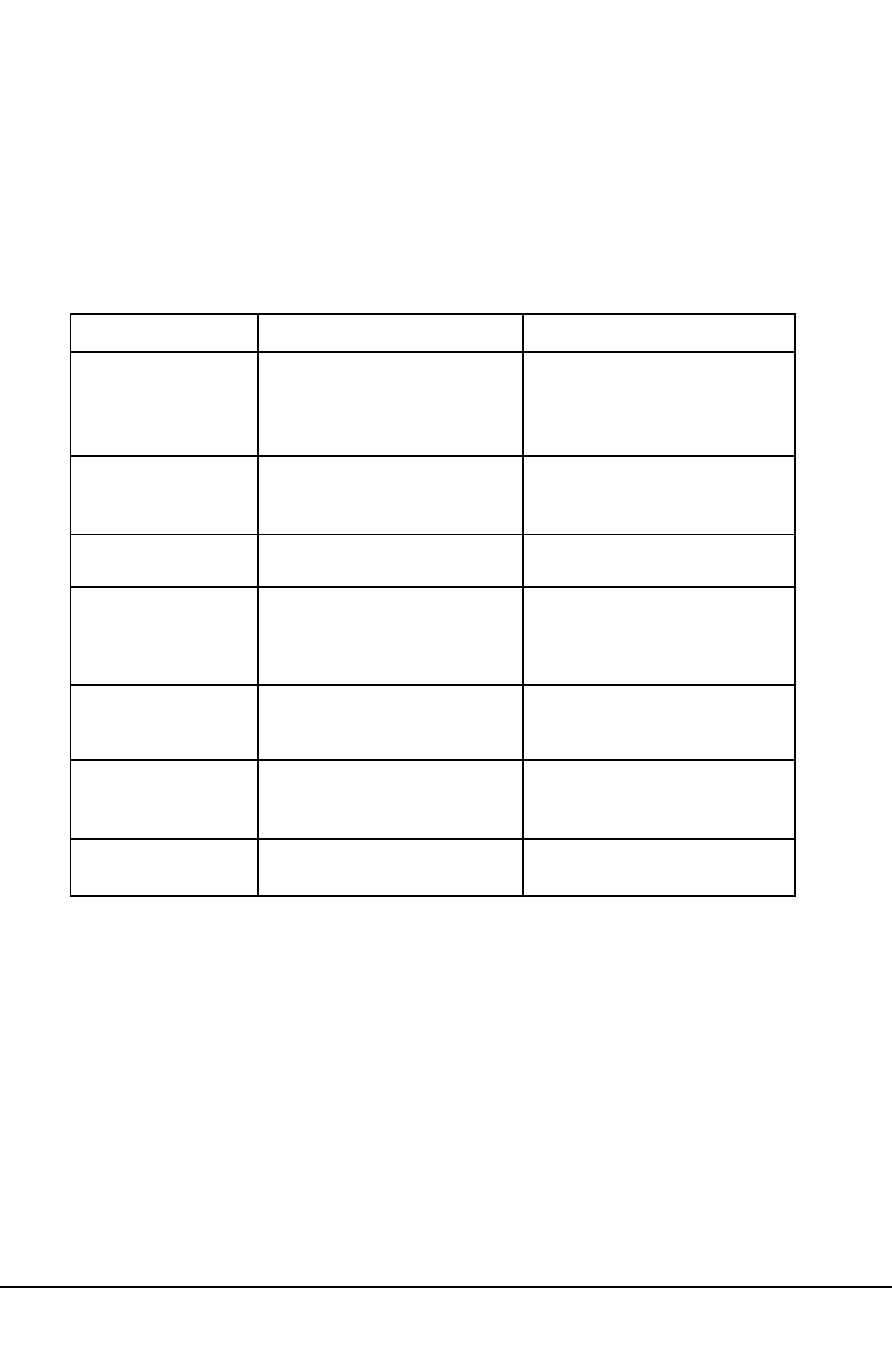
In his book Power Quality Primer, Barry Kennedy provided information on different types of power
quality problems. Some of that information is summarized in Table 1.3 below.
Table 1.3: Typical Power Quality Problems and Sources
Q
It is often assumed that power quality problems originate with the utility. While it is true that may
power quality problems can originate with the utility system, many problems originate with
customer equipment. Customer-caused problems may manifest themselves inside the customer
location or they may be transported by the utility system to another adjacent customer. Often,
equipment that is sensitive to power quality problems may in fact also be the cause of the problem.
Q
If a power quality problem is suspected, it is generally wise to consult a power quality professional
for assistance in defining the cause and possible solutions to the problem.
Electro Industries/GaugeTech
Doc # E107706 V1.25 1-13
Cause Disturbance Type Source
Impulse Transient
Transient voltage disturbance,
sub-cycle duration
Oscillatory transient
with decay
Lightning
Electrostatic discharge
Load switching
Capacitor switching
Sag / swell
Interruptions
Undervoltage /
Overvoltage
Voltage flicker
Harmonic distortion
Transient voltage, sub-cycle
duration
RMS voltage, multiple cycle
duration
RMS voltage, multiple second or
longer duration
RMS voltage, steady state,
multiple second or longer
duration
RMS voltage, steady state,
repetitive condition
Steady state current or voltage,
long term duration
Line/cable switching
Capacitor switching
Load switching
Remote system faults
System protection
Circuit breakers
Fuses
Maintenance
Motor starting
Load variations
Load dropping
Intermittent loads
Motor starting
Arc furnaces
Non-linear loads
System resonance


















