Vigor3300 Series User’s Guide
54
3
3
.
.
3
3
.
.
2
2
N
N
A
A
T
T
S
S
e
e
t
t
u
u
p
p
NAT (Network Address Translation) is a method of mapping one or more IP addresses and/or
service ports into different specified services. It allows the internal IP addresses of many
computers on a LAN to be translated to one public address to save costs and resources of
multiple public IP addresses. It also plays a security role by obscuring the true IP addresses of
important machines from potential hackers on the Internet. The Vigor 3300 Series is
NAT-enabled by default and gets one globally routable IP addresses from the ISP by Static,
PPPoE, or DHCP mechanism. The Vigor3300 Series assigns private network IP addresses
according to RFC-1918 protocol and translates the private network addresses to a globally
routable IP address so that local hosts can communicate with the router and access the
Internet.
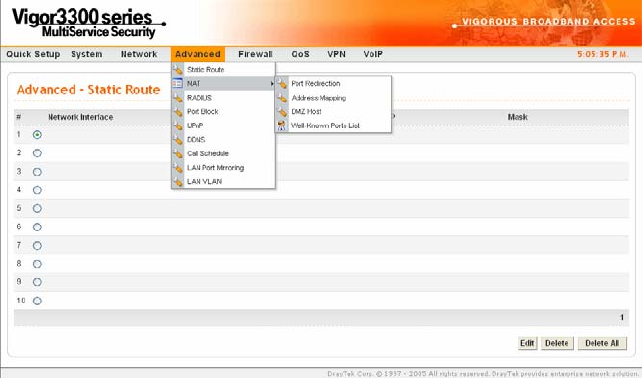
In the Advanced group, click the NAT option.
There are four functions that NAT provides – Port Redirection, Address Mapping, DMZ
Host and Well-Known Parts List.
P
P
o
o
r
r
t
t
R
R
e
e
d
d
i
i
r
r
e
e
c
c
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
Port Redirection means port forwarding. It may be used to expose internal servers to the
public domain or open a specific port to internal hosts. Internet hosts can use the WAN IP
address to access internal network services, such as FTP, WWW and etc. The internal FTP
server is running on the local host addressed as 192.168.1.2. When other users send this type
of request to your network through the Internet, the router will direct these requests to an
appropriate host inside. A user can also translate the port to another port by configuration. For
example, port number with 1024 can be transferred into IP address of 192.168.1.100 of LAN.
The packet is forwarded to a specific local host if the port number matches that defined in the
table. In the Advanced group, move to NAT option and choose Port Redirection to get the
corresponding page.