2.1.2.6 Bias Voltages and Laser Drive Timing
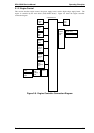
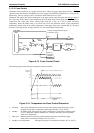
Figure 2-19 is a diagram of the drum charge bias voltage, image transfer bias voltage, and the developing
bias voltage control circuit. These bias voltages are generated from the +24 VDC from the high-voltage
supply board (PWB-F). If the printer detects a case-open condition, the interlock switch is set to off, which
cuts the +24 VDC, which, in turn, cuts the bias voltages.
These bias voltages are controlled by the main board (C180 MAIN). The
HV-T signal is the image transfer
bias voltage control. While this signal is LOW, the image transfer electrode comb is charged to from +3 to
+6K VDC by the high-voltage supply circuit.
HV SEL1 and HV SEL2 are image transfer bias level control
signals.
The HVB signal is the digital signal for developing bias voltage control. This signal controls the bias on/off.
The BIAS MON signal controls the bias voltage level (–300 V to –375K VDC) using pulse data. The image
density is controlled by the developing bias voltage level.
+24 VDC
Interlock
SW
Power Supply
Board
(PWB-E)
+24 VDC
HV-C
HV-T
HV SEL1
Image Transfer
Bias
3K to 6 K VDC
Developing
Bias
-270 to -370 VDC
Drum Charge
-2.0 K VDC
Main
Board
(C180 MAIN)
High Voltage Supply
Board
(PWB-F)
Toner Doctor Blade
Bias -500 VDC
HV SEL2
HV B
BIAS MON
Seal Bias
-250 VDC
PWB-S
Figure 2-19. High-Voltage Supply Block Diagram
EPL-5500W Service Manual Operating Principles
Rev. A 2-13