Command Specifications
3 -
68
C141-E167
Note:
Even when there is an error in the specification in the CDB, or when a write operation to the disk
media cannot be executed normally due to various other causes, the transfer of data (data is pre-
fetched to the data buffer) from the INIT to the IDD may be executed. In this case, the length of
data transferred from the INIT to the IDD is undefined. Also, all the data transferred to the IDD
will not necessarily be actually written to the disk media. However, if the command is
terminated with a CHECK CONDITION status and the sense key of the sense data indicates
"ILLEGAL REQUEST [=5]," the data from that command is not written to the disk media by a
write operation.
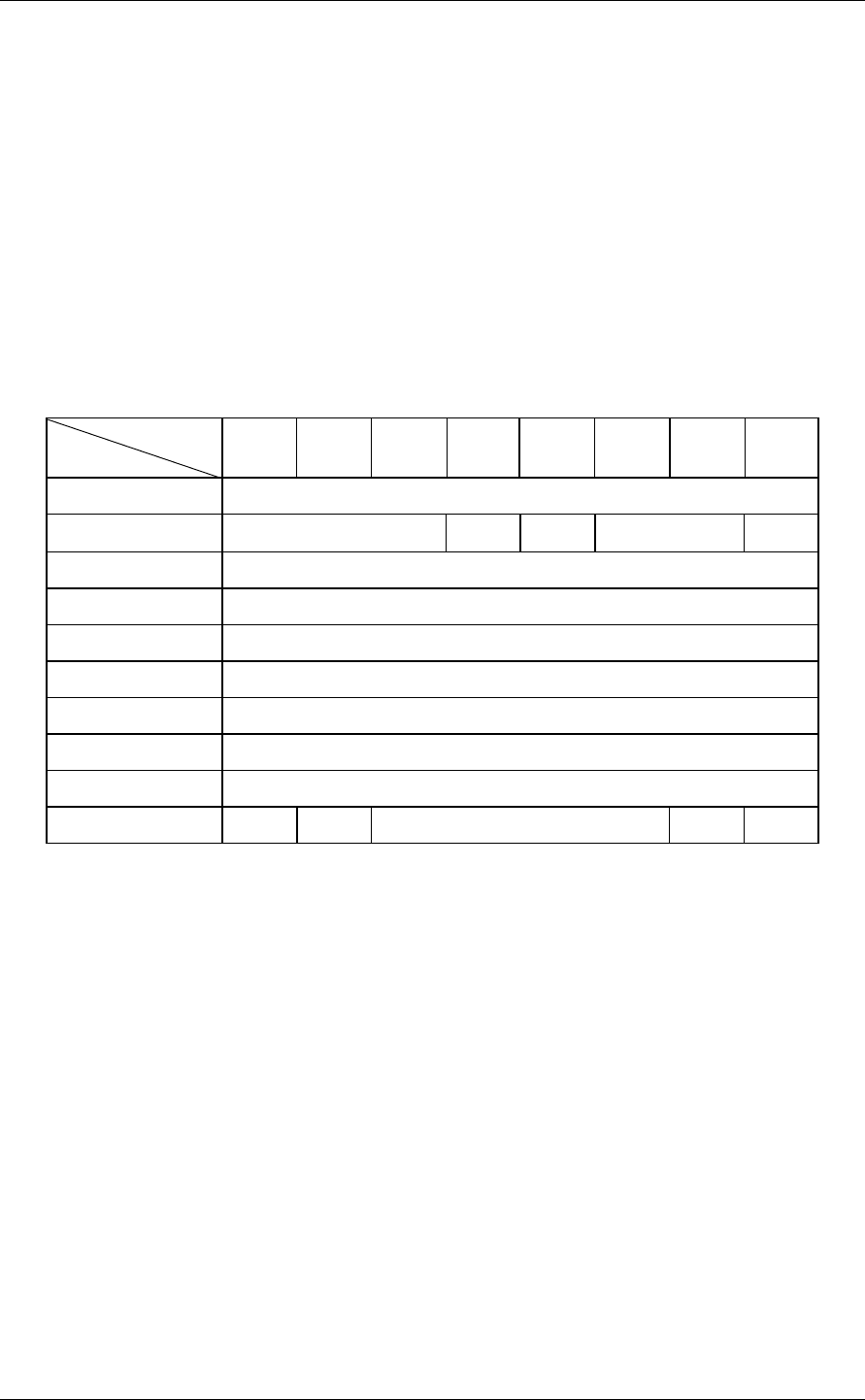
3.2.4 WRITE EXTENDED (2A)
Bit
Byte
76543210
0X‘2A’
1LUN
×
FUA 0 0 0
2 Logical Block Address (MSB)
3 Logical Block Address
4 Logical Block Address
5 Logical Block Address (LSB)
6 00000000
7 Transfer Block Count (MSB)
8 Transfer Block Count (LSB)
9 0000000Link
This command transfers the number of blocks of data specified in the "Transfer block count" field
from the INIT and writes them in continuous logical data blocks with the logical data block on the
disk media specified in the "Logical block address" field in the CDB as the top.
The functions of this command are the same as those of the Group 0 WRITE command (Section
3.2.3) with the exception that it is possible to specify 4-byte logical block addresses and 2-byte
transfer block counts. However, when zero is specified for the "Transfer block count," the command
is terminated normally without pre-fetch being performed.
• FUA (force unit access)
When this bit is "0", it indicates that the IDD satisfy the command by accessing the cache
memory. For write operations, logical blocks may be transferred directly to the cache memory.
GOOD status may be returned to the INIT prior to writing the logical blocks to the medium. Any
error that occurs after the GOOD status is returned is a deferred error and information regarding
the error is not reported until a subsequent command.


















