142
■ Extended Intelligent I/O Service (EI
2
OS)
•In addition to programming being made
easier, because there in no need to
execute unnecessary program transfers
higher speeds for transfer service
response and overall system control are
realized.
•Since CPU micro-instructions execute
transfer functions, multi-channel systems
can be realized at no extra cost.
•Since I/O transfers can be stopped when
a condition is generated such as when
invalid data is received, performance loss
due to transfering unnecessary data can
be avoided because there is no
programming load.
•It is possible to specify incrementing or
decrementing of buffer addresses and
I/O register addresses can be specified.
•It is possible to specify the entire 00 bank
as I/O register addresses.
•It is possible to specify the data counter
to count up to 64K.
•Execution speed
From request to completion of transfer:
28 cycles = 1.75µs (@16 MHz)
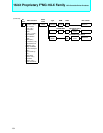
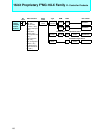
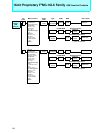
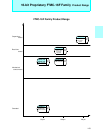
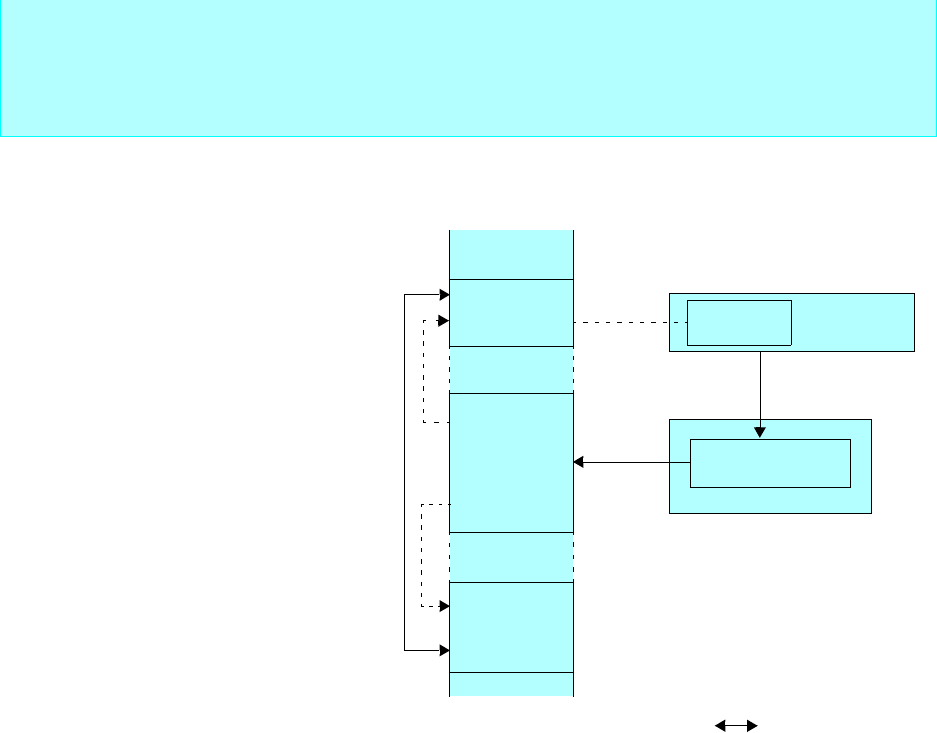
Memory space
I/O registers
IOA
(I/O address)
ISD
BAP
(Memory address)
Memory
I/O register
ICS
Interrupt controller
Interrupt control register
Peripheral
2 Interrupt requests
1
3
3
4
Operation mechanism
1. An I/O transfer request is generated.
2. The interrupt controller selects a descriptor.
3.Transfer source and destination addresses
are read out of the descriptor.
4.Data is transferred from I/O register to mem-
ory space.
I/O
(000000
H to 00FFFFH)
Memory
(000000
H to FFFFFFH)
16-bit Proprietary F
2
MC-16F Family
Extended intelligent I/O Service