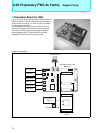
86
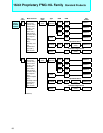
■ Extended Intelligent I/O Service (EI
2
OS)
• In addition to programing being made easier because htere is no need to execute unnecessary program trans-
fers, higher speeds for transfer, service response and overall system controls are realized.
• Since CPU micro-instructions executs transfer functions, multi-channel systems can be realized at no extra cost.
• Since I/O transfers can be stopped when a condition is generated such as when invalid data is received,
performance loss due to transferring unnecessary data can be avoided because there is no programming load.
• It is possible to specify incrementing or decrementing of buffer address and I/O register address.
• It is possible to specify the entire 00 banks I/O register addresses, the data counter can be set up to 64000.
• Execution speed
From request, to completion of transfer: 32 cycles = 2.00 µs (@16 MHz)
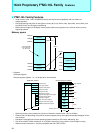
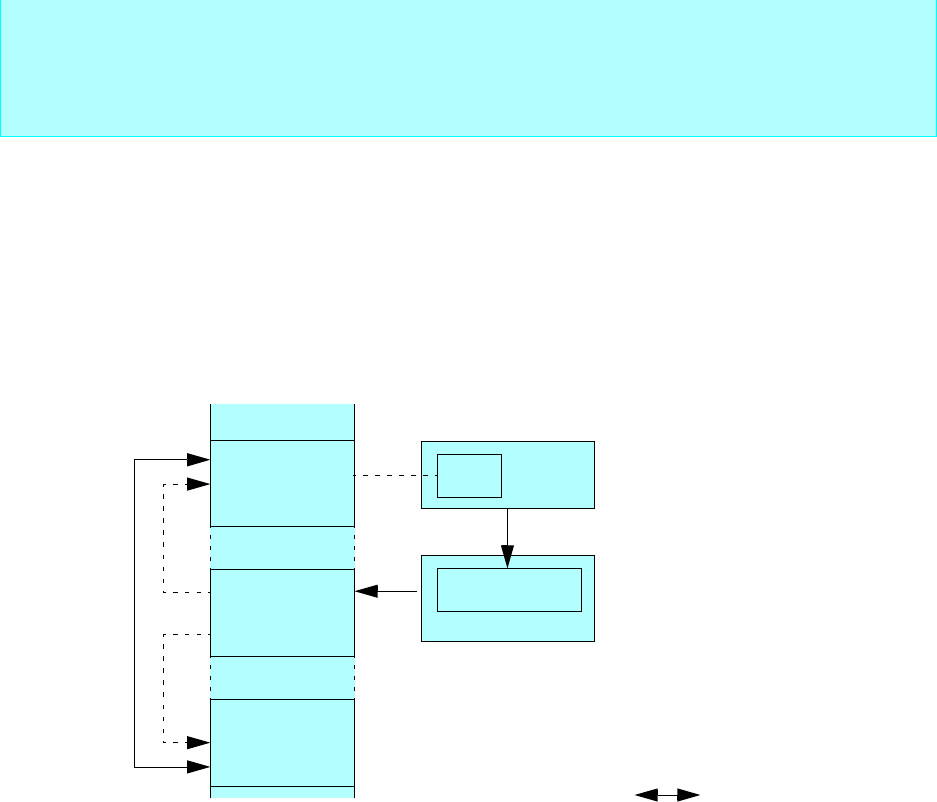
ISD
Memory space
I/O registers
Memory
IOA
(I/O address)
BAP
(memory address)
3
3
4
ICS
Interrupt controller
Interrupt control register
Peripheral
I/O
register
2 interrupt requests
1
Operation mechanism
1. An I/O transfer request is generated.
2. The interrupt controller selects the descriptor.
3. Transfer source and destination addresses are read out of the
descriptor.
4. Data is transferred between I/O register and memory space.
I/O
(000000
H to 0000FFH) (000000H to FFFFFFH)
Memory
16-bit Proprietary F
2
MC-16L Family
Extended Intelligent I/O Service