6-10
IPv6 Management Security Features
Authorized IP Managers for IPv6
■ Each authorized station has the same 64-bit device ID (244:17FF:FEB6:D37D)
because the value of the last four blocks in the mask is FFFF (binary value
1111 1111).
FFFF requires all bits in each corresponding block of an authorized IPv6
address to have the same “on” or “off” setting as the device ID in the
specified IPv6 address. In this case, each bit in the device ID (last four
blocks) in an authorized IPv6 address is fixed and can be only one value:
244:17FF:FEB6:D37D.
Figure 6-6. Example: Mask for Configuring Authorized IPv6 Manager Stations in Different Subnets
Figure 6-7. Example: How a Mask Determines Authorized IPv6 Manager Addresses by Subnet
1st
Block
2nd
Block
3rd
Block
4th
Block
5th
Block
6th
Block
7th
Block
8th
Block
Manager- or Operator-Level Access
IPv6 Mask FFFF FFFF FFFF FFF8 FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF In this example, the IPv6 mask allows up
to four stations in different subnets to
access the switch. This authorized IP
manager configuration is useful if only
management stations are specified by
the authorized IPv6 addresses. Refer to
Figure 6-4 for how the bitmap of the IPv6
mask determines authorized IP manager
stations.
Authorized
IPv6 Address
2001 DB8 0000 0000 244 17FF FEB6 D37D
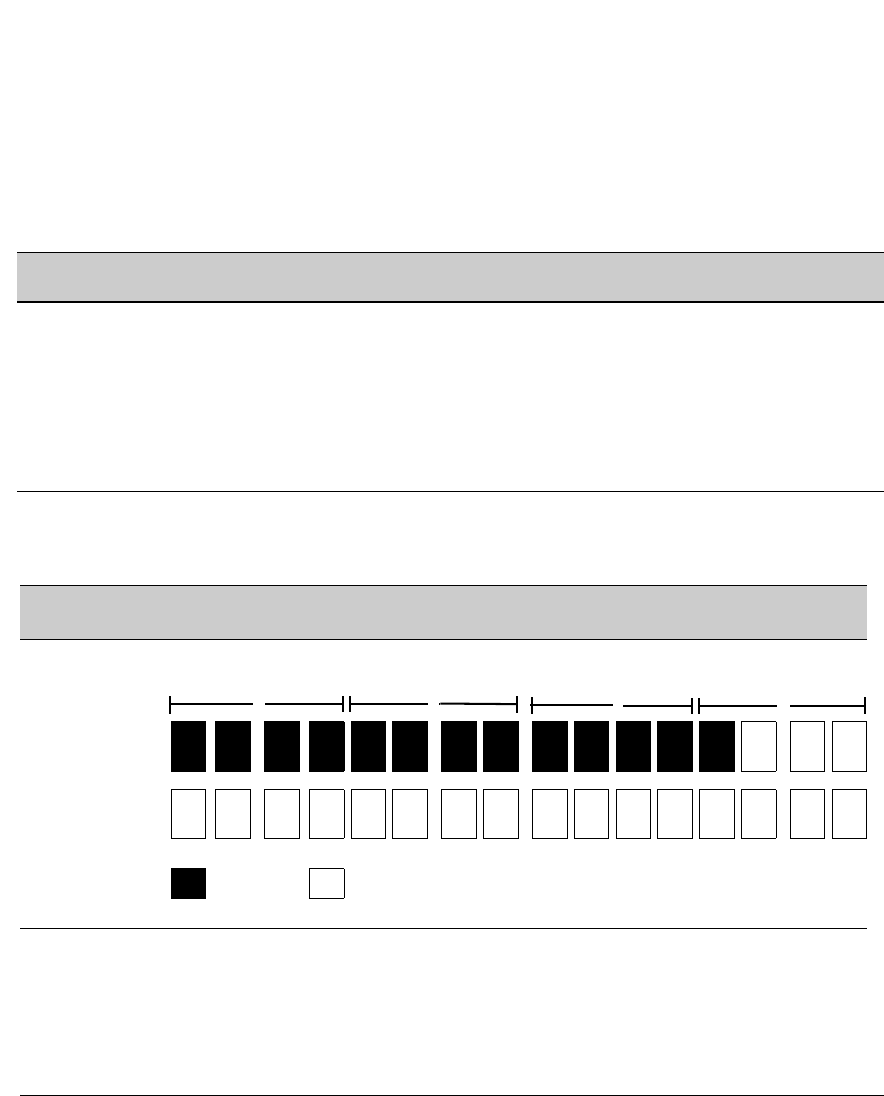
Fourth Block in Mask: FFF8
Fourth Block in Prefix ID of IPv6 Address: 0000
Bit Numbers Bit
15
Bit
14
Bit
13
Bit
12
Bit
11
Bit
10
Bit
9
Bit
8
Bit
7
Bit
6
Bit
5
Bit
4
Bit
3
Bit
2
Bit
1
Bit
0
Bit Value F F F
8
FFF8: Fourth Block
in Mask
0000: Fourth Block
in IPv6 Address
Bit Setting:
= 1 (On) = 0 (Off)


















