3-22
IPv6 Addressing
Multicast Application to IPv6 Addressing
For information on Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) refer to the chapter
titled “Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) Snooping”.
When MLD is enabled on an interface, you can use show ipv6 mld [ vlan < vid >]
to list the active multicast group activity the switch has detected per interface
from other devices.
IPv6 Multicast Address Format
The multicast address format has three principal sections in the leading 16
bits:
■ identifier: ff (bits 1-8)
■ flags: 0xxx (bits 9-12)
■ scope: 0001 - 1110 (bits 13-16)
For related information, refer to RFC 4291.
Multicast Group Identification
■ multicast identifier: The first eight high-order bits, set to ff, identify the
address as multicast.
■ multicast flags: Bits 9-12 are multicast flags that provide additional
information about the multicast address, as follows:
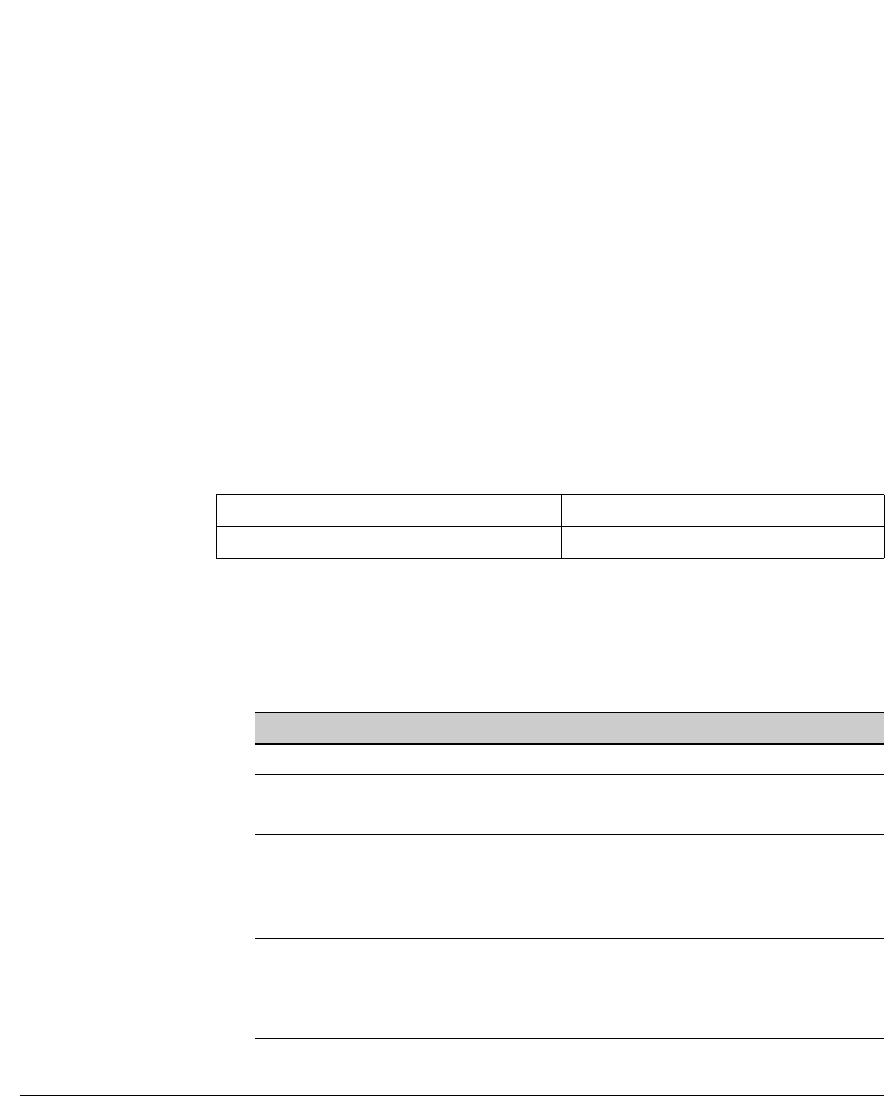
Multicast ID, Flags and Scope (16 bits) Group Identifier (112 bits)
1111 1111 0xxx xxxx :
x...x : x...x : x...x : x...x : x...x : x...x : x...x
Bit ID Options Use
9 0 reserved
10 (R) 0 multicast address without PIM-SM rendezvous point
1 multicast address with PIM-SM rendezvous point
11 (P) 0 multicast address without prefix information from the
originating network
1 multicast address with prefix information from the originating
network
12 (T) 0 multicast address is permanent (well-known, and not
restricted by scope value)
1 multicast address is temporary (and used only within an
identified scope)


















