Rate Limiting
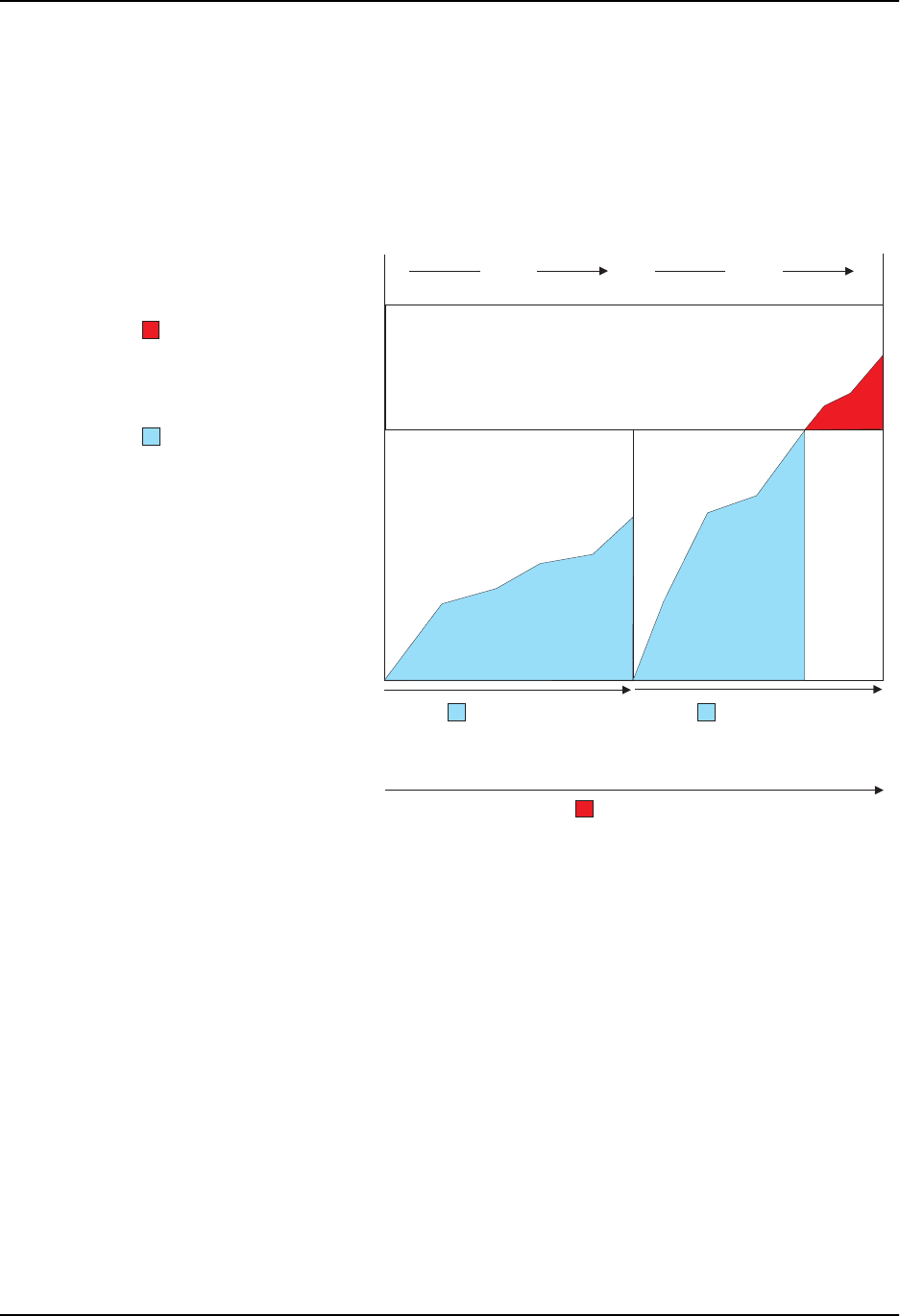
Figure 4.5 shows an example of the Normal Burst Size and Excess Burst Size counters. This example shows two
Committed Time Intervals.
Line rate = 1,000,000,000 bps (one Gigabit)
Average Rate = 500,000,000 bits
Normal Burst Size = 62,500,000 bytes (500,000,000 bits)
Excess Burst Size = 93,750,000 bytes (750,000,000 bits)
Committed Time Interval = 1 second
1000Mbps port
Excess Burst packets - received after
maximum number of Normal Burst
packets are received within the Committed
Time Interval. The Exceed action applies to
these packets.
Excess Burst Counter restarts at zero at
the beginning of every second Committed
Time Interval.
Normal Burst packets -The Conform action
applies to these packets.
Normal Burst Counter restarts at zero at
the beginning of each Committed Time Interval.
One second
One second
Zero - 500,000,000
Zero - 500,000,000
bits of packet data
bits of packet data
300,000,000 bits received
500,000,000 bits received
in this Committed Time
in this Committed Time
Interval
Interval
500,000,001 - 750,000,000
bits of packet data
None received in first
Committed Time Interval
175,000,000 bits received in
second Committed Time
Interval
Figure 4.5 Normal and Excess Burst Size Counters
Notice that the counter for the Normal Burst Size counter restarts at the beginning of each Committed Time
Interval, whereas the counter for the Excess Burst Size restarts after every two Committed Time Intervals. In this
example, the policy rule on the interface matches 300,000,000 bits of Ethernet traffic data during the first
Committed Time Interval. Therefore, all the traffic conformed to the policy rule and the software took the action
specified for conforming traffic.
During the second Committed Time Interval, the policy rule on the interface matches 675,000,000 bits of Ethernet
traffic data. Since the Normal Burst Size is 500,000,000, the software takes the conforming action for the first
500,000,000 bits. However, the software takes the exceed action for the remaining traffic. In this example, the
action for conforming traffic is to set the IP precedence to 5, then forward the traffic. The action for exceed traffic
is to set the IP precedence to 0, then forward the traffic.
4 - 11


















