EM78P447N
8-Bit Microcontroller with OTP ROM
Product Specification (V1.1) 03.30.2005
• 25
(This specification is subject to change without further notice)
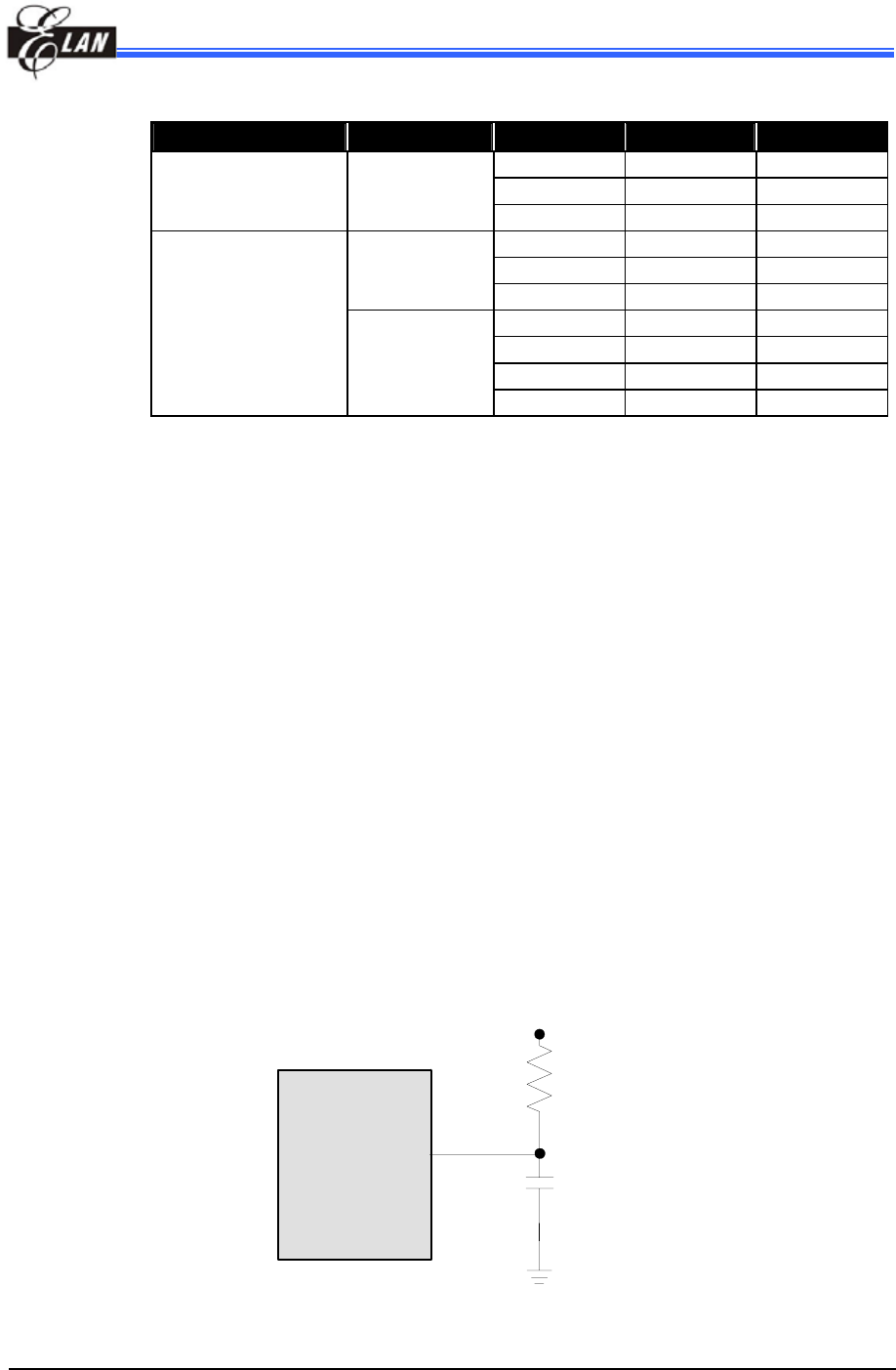
Table 12 Capacitor Selection Guide for Crystal Oscillator or Ceramic Resonator
Oscillator Type Frequency Mode Frequency C1(pF) C2(pF)
455 kHz 100~150 100~150
2.0 MHz 20~40 20~40
Ceramic Resonators HXT
4.0 MHz 10~30 10~30
32.768kHz 25 15
100KHz 25 25
LXT
200KHz 25 25
455KHz 20~40 20~150
1.0MHz 15~30 15~30
2.0MHz 15 15
Crystal Oscillator
HXT
4.0MHz 15 15
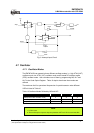
4.7.3 External RC Oscillator Mode
For some applications that do not need a very precise timing calculation, the RC
oscillator (Fig. 15) offers a lot of cost savings. Nevertheless, it should be noted that the
frequency of the RC oscillator is influenced by the supply voltage, the values of the
resistor (Rext), the capacitor (Cext), and even by the operation temperature.
Moreover, the frequency also changes slightly from one chip to another due to the
manufacturing process variation.
In order to maintain a stable system frequency, the values of the Cext should not be
less than 20pF, and that the value of Rext should not be greater than 1 M ohm. If they
cannot be kept in this range, the frequency is easily affected by noise, humidity, and
leakage.
The smaller the Rext in the RC oscillator, the faster its frequency will be. On the
contrary, for very low Rext values, for instance, 1 KΩ, the oscillator becomes unstable
because the NMOS cannot discharge the current of the capacitance correctly.
Based on the above reasons, it must be kept in mind that all of the supply voltage, the
operation temperature, the components of the RC oscillator, the package types, the
way the PCB is layout, will affect the system frequency.
OSCI
EM78P447S
VCC
Rext
Cext
Fig. 12 External RC Oscillator Mode Circuit