Chapter 2. Architecture and technical overview 59
IVM cannot be used by HACMP software to activate Capacity on Demand (CoD)
resources on machines that support CoD.
IVM provides advanced virtualization functionality without the need for an extra-cost
workstation. For more information about IVM functionality and best practices, see Virtual I/O
Server Integrated Virtualization Manager, REDP-4061 at this Web site:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/p/hardware/meetp5/ivm.pdf
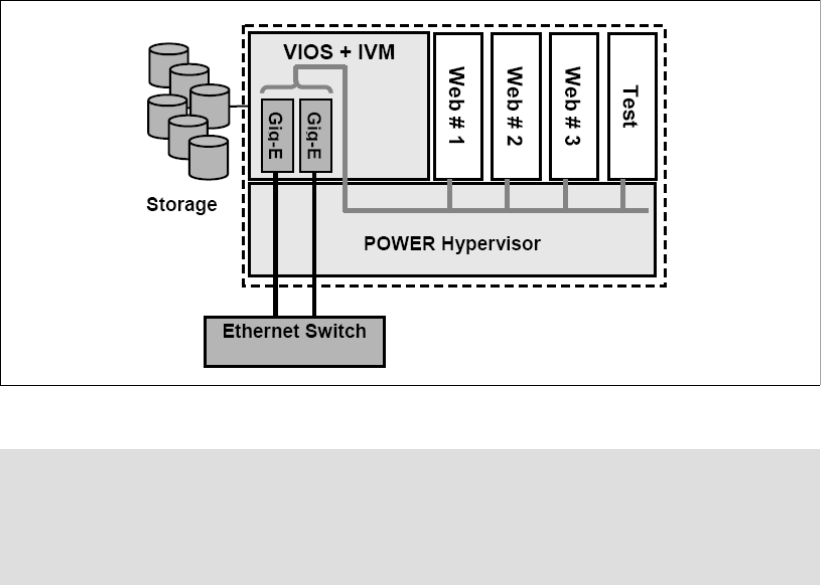
Figure 2-16 shows how a system with IVM is organized. There is a Virtual I/O Server and IVM
installed in one partition that owns all of the physical server resources and four client
partitions. IVM communicates to the POWER Hypervisor to
create, manage, and provide
virtual I/O
for client partitions. But the dispatch of partitions on physical processors is done
by the POWER Hypervisor as in HMC-managed servers. The rules for mapping the physical
processors, virtual processors, and logical processors apply for shared partitions managed by
the HMC as discussed in 2.12.2, “Logical, virtual, and physical processor mapping” on
page 52.
Figure 2-16 IVM principles
Operating system support for advanced virtualization
Table 2-13 on page 60 lists AIX 5L and Linux support for advanced virtualization.
Note: IVM and HMC are two separate management systems and cannot be used at the
same time. IVM targets ease of use, while HMC targets flexibility and scalability. The
internal design is so different that you should never connect an HMC to a working IVM
system. If you want to migrate an environment from IVM to HMC, you have to rebuild the
configuration setup manually.


















