Chapter 3. RAS and manageability 79
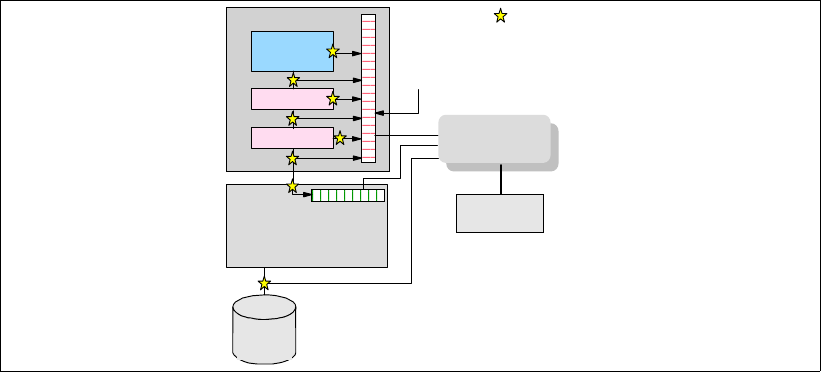
Figure 3-1 Schematic of Fault Isolation Register implementation
The FIRs are important because they enable an error to be uniquely identified, thus enabling
the appropriate action to be taken. Appropriate actions might include such things as a bus
retry, ECC correction, or system firmware recovery routines. Recovery routines can include
dynamic deallocation of potentially failing components.
Errors are logged into the system non-volatile random access memory (NVRAM) and the
service processor event history log, along with a notification of the event to AIX 5L for capture
in the operating system error log. Diagnostic Error Log Analysis (
diagela) routines analyze
the error log entries and invoke a suitable action such as issuing a warning message. If the
error can be recovered, or after suitable maintenance, the service processor resets the FIRs
so that they can record any future errors accurately.
The ability to correctly diagnose any pending or firm errors is a key requirement before any
dynamic or persistent component deallocation or any other reconfiguration can take place.
For further details, see 3.1.7, “Resource deallocation” on page 81.
3.1.3 Permanent monitoring
The service processor (SP) included in the p5-520 or p5-520Q provides a way to monitor the
system even when the main processor is inoperable.
Mutual surveillance
The SP can monitor the operation of the firmware during the boot process, and it can monitor
the operating system for loss of control. This allows the service processor to take appropriate
action, including calling for service, when it detects that the firmware or the operating system
has lost control. Mutual surveillance also allows the operating system to monitor for service
processor activity and can request a service processor repair action if necessary.
Environmental monitoring
Environmental monitoring related to power, fans, and temperature is done by the System
Power Control Network (SPCN). Environmental critical and non-critical conditions generate
Early Power-Off Warning (EPOW) events. Critical events (for example, Class 5 ac power loss)
trigger appropriate signals from the hardware to the impacted components in order to prevent
any data loss without the operating system or firmware involvement. Non-critical
environmental events are logged and reported using Event Scan.
CPU
L1 Cache
L2/L3 Cache
Memory
F
ault
I
solation
R
egister
(FIR)
(unique fingerprint of each
error captured)
Service
Processor
Non-volatile
RAM
Error Checkers
Log Error
Disk


















