Reference Thermal Solution
R
24 Intel
®
955X Express Chipset Thermal/Mechanical Design Guide
6.5.4.1 Effect of Pressure on TIM Performance
As mechanical pressure increases on the TIM, the thermal resistance of the TIM decreases. This
phenomenon is due to the decrease of the bond line thickness (BLT). BLT is the final settled
thickness of the thermal interface material after installation of heatsink. The effect of pressure on
the thermal resistance of the Honeywell* PCM45F TIM is shown in Table 6-1. The heatsink clip
provides enough pressure for the TIM to achieve a thermal conductivity of 0.17 °C inch
2
/W.
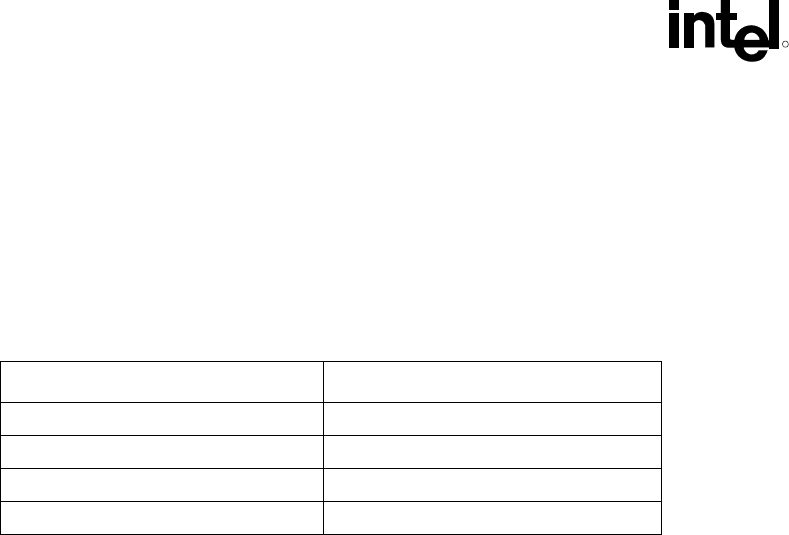
Table 6-1 Honeywell PCM 45F TIM Performance as a Function of Attach Pressure
Pressure (psi) Thermal Resistance (°C × in
2
)/W
5 0.049
10 0.046
20 0.045
30 0.044
Note: All measured at 50 °C.
6.5.5 Heatsink Clip
The retention mechanism in this reference solution includes two different types of clips; one is
ramp clip and the other is wire clip. Each end of the wire clip is attached to the ramp clip that in
turn attaches to anchors to fasten the overall heatsink assembly to the motherboard. See
Appendix B for a mechanical drawing of the clip.
6.5.6 Clip Retention Anchors
For 955X Express chipset-based platforms that have very limited board space, a clip retention
anchor has been developed to minimize the impact of clip retention on the board. It is based on a
standard two-pin jumper and is soldered to the board like any common through-hole header. A
new anchor design is available with 45° bent leads to increase the anchor attach reliability over
time. See Appendix A for the part number and supplier information.
