44
● Encryption mode
Setting for encrypting the flow of data during wireless communication.
Following settings are available:
None (Open System): No encryption. Setting will be unavailable and throughput will be improved. However, there is the risk of infor-
mation leakage.
40blt WEP: Encryption is performed using 40-blt encryption key.
128blt: Encryption is performed using 104-blt + 24-blt (1V) keys. Although throughput will decline compared to Open
System, security of data will be improved.
● Access point (wireless LAN)
Relay point for infrastructure communication. It can also serve as the relay point for cable LAN or wireless LAN.
● ASF (Advanced Streaming Format)
Data streaming format developed by Microsoft Corporation (U.S.) for transmission of video and audio.
● Host name
Name of a device (not limited to a computer but all connection devices with an IP address) on a network.
● Port number
Number used for detecting applications and service during TCP/IP communication.
● TCP/IP
Abbreviation for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol and is one of the protocols used during network connection.
● UDP
Different from TCP, UDP is a low-level protocol that does not perform receive checks. In some cases, missing and distorted images
may occur due to packet loss.
Others
Terminology
45
Others
Terminology
\About IP address
Global IP address and local IP address
There are 2 types of IP addresses: “global IP address” and “local IP address”.
Global IP address: Just as different IP addresses are needed on a network, all PCs using the Internet worldwide must use a unique
IP address. This IP address is referred to as “global IP address”.
Normally, the global address is assigned by the IS provider.
Local IP address: In an environment not connected to the Internet (within a household, within a company, etc.), separate IP
addresses can be used freely within a network.
This IP address is referred to as “local IP address”.
IP address classes
IP addresses are categorized into 3 classes depending on the number of PCs structuring a network.
“Class A IP addresses” are used for large-scale networks, “Class B IP addresses” are used for medium-scale networks and “Class C
IP addresses” are used for small-scale networks.
Within a network, all IP addresses must be of the same class. Each IP address is structured by a series of 4 digit numbers separated
by a period. The first number of the IP address indicates the class.
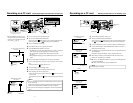
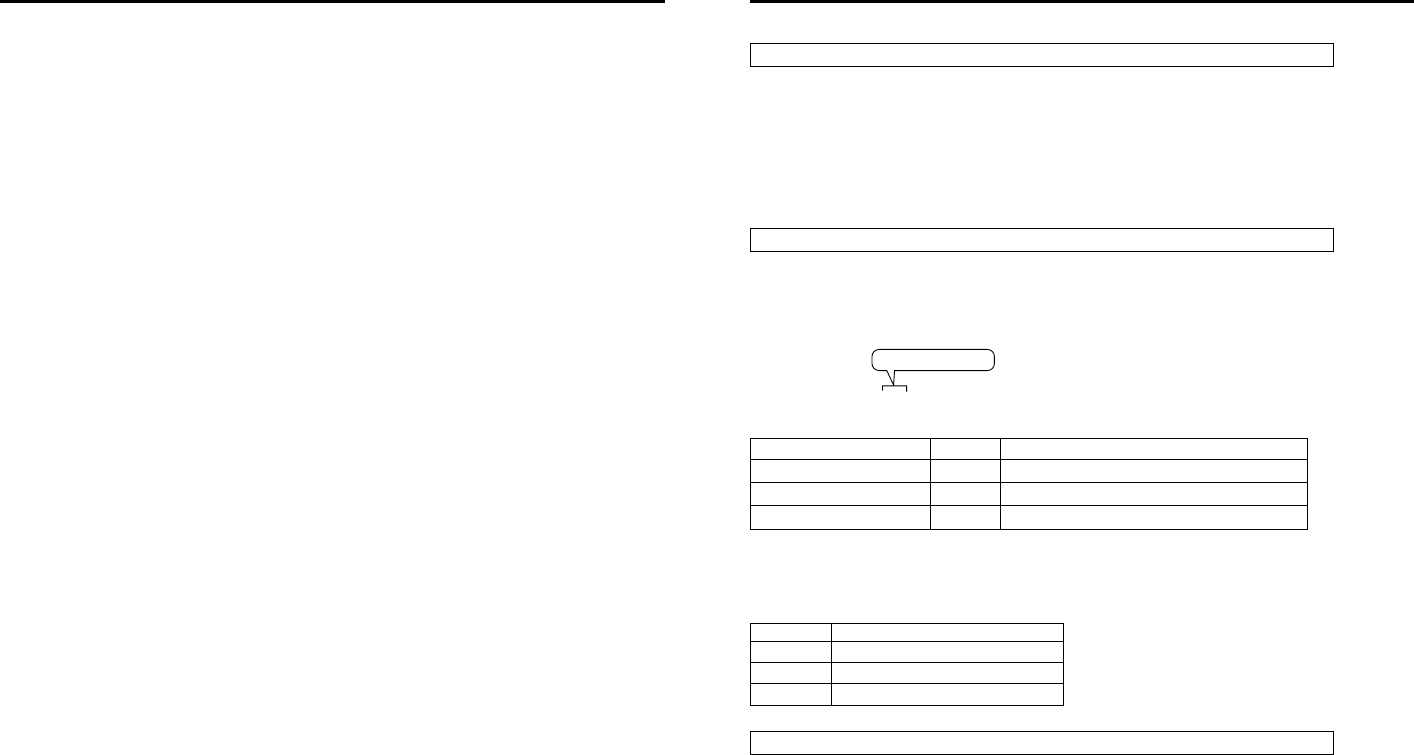
First number of the IP address Class Application (number of PCs structuring the network)
1~127 Class A For large-scale networks (max. approx. 16 million units)
128~191 Class B For medium-scale networks (max. approx. 65,000 units)
192~223 Class C For small-scale networks (max. approx. 120 units)
* “224 ~ 255” are normally not used for IP addresses.
For example, a network structured by a few PCs to dozens of PCs would use Class C IP addresses.
Normally, the following special IP addresses are used when structuring a network.
Class indicated here
IP address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Class Set IP address
Class A 10.0.0.0 ~ 10.255.255.255
Class B 172.16.0.0 ~ 172.31.255.255
Class C 192.168.0.0 ~ 192.168.255.255
About proxy server
A proxy is a “relay point” for accessing the Internet. When enabling “Use a proxy server”, the proxy server will make access to the
Internet.
Since various access information is cached at this time, downloading will be faster when reloading the same information from the
Internet since the data is loaded from the proxy server.