149
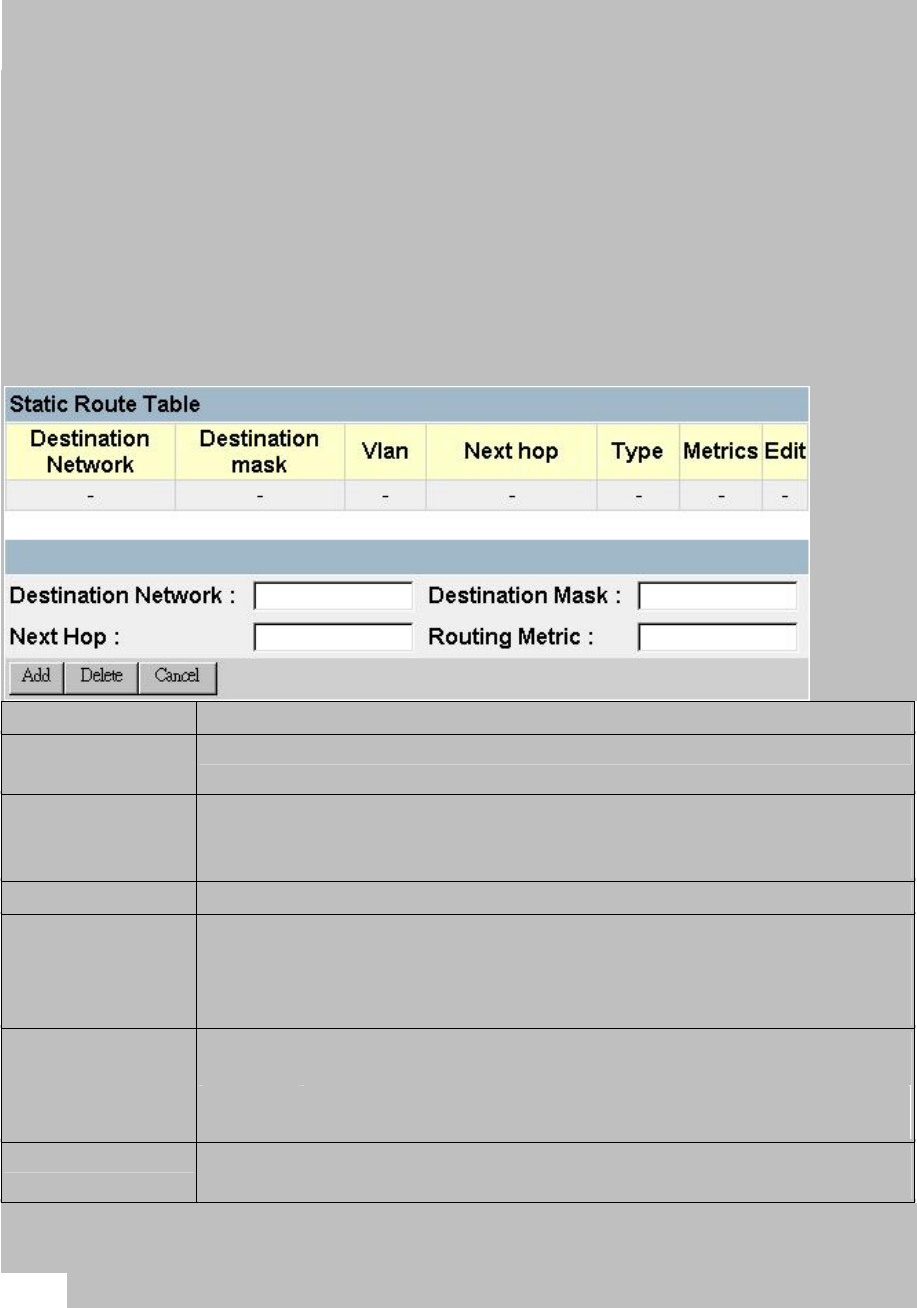
3.6.6.4.Static Route Configuration
This switch can be configured to dynamically learn the routes to other IP networks,
subnets or hosts using unicast or multicast routing protocols. If the route to a specific
destination cannot be learned via these protocols, or you wish to restrict the path used
for transmitting traffic to a destination, it can be statically configured using the Static
Route Table.
Before defining a static route, remember that you must first configure at least one IP
interface on this switch (chapter 3 “Subnet Configuration”). Static routes take
precedence over dynamically learned routes and remain in the table until you remove
them or the corresponding IP interface from this switch.
Parameter Description
Destination
Network
A destination network, subnet or host.
Destination Mask The subnet mask that specifies the bits to match. A routing entry will
be used for a packet if the bits in the address set by the destination
mask match the Destination Network.
VLAN The VLAN within which the gateway or destination address resides.
Next Hop The IP address of the router at the next hop.
Note that the network portion of the next hop must match that used
for one of the subnet IP interfaces configured on this switch. (See
“Subnet Configuration” on chapter 3.)
Type The IP route type for the destination network. This switch supports
the following types:
Direct: A directly connected subnetwork.
Indirect: A remote IP subnetwork or host address.
Routing Metric*
A
relative measure of the path cost from this switch to the destination
network.
*This value depends on the specific routing protocol.
Note:
To add a static route, specify it in the dialog boxes at the bottom of the screen,


















