162
MAC Address MAC address that maps to the corresponding IP address.
VLAN The VLAN group to which this host has been assigned.
Port The port this to which host device is attached. (Port “0” refers to an
interface defined on this switch.)
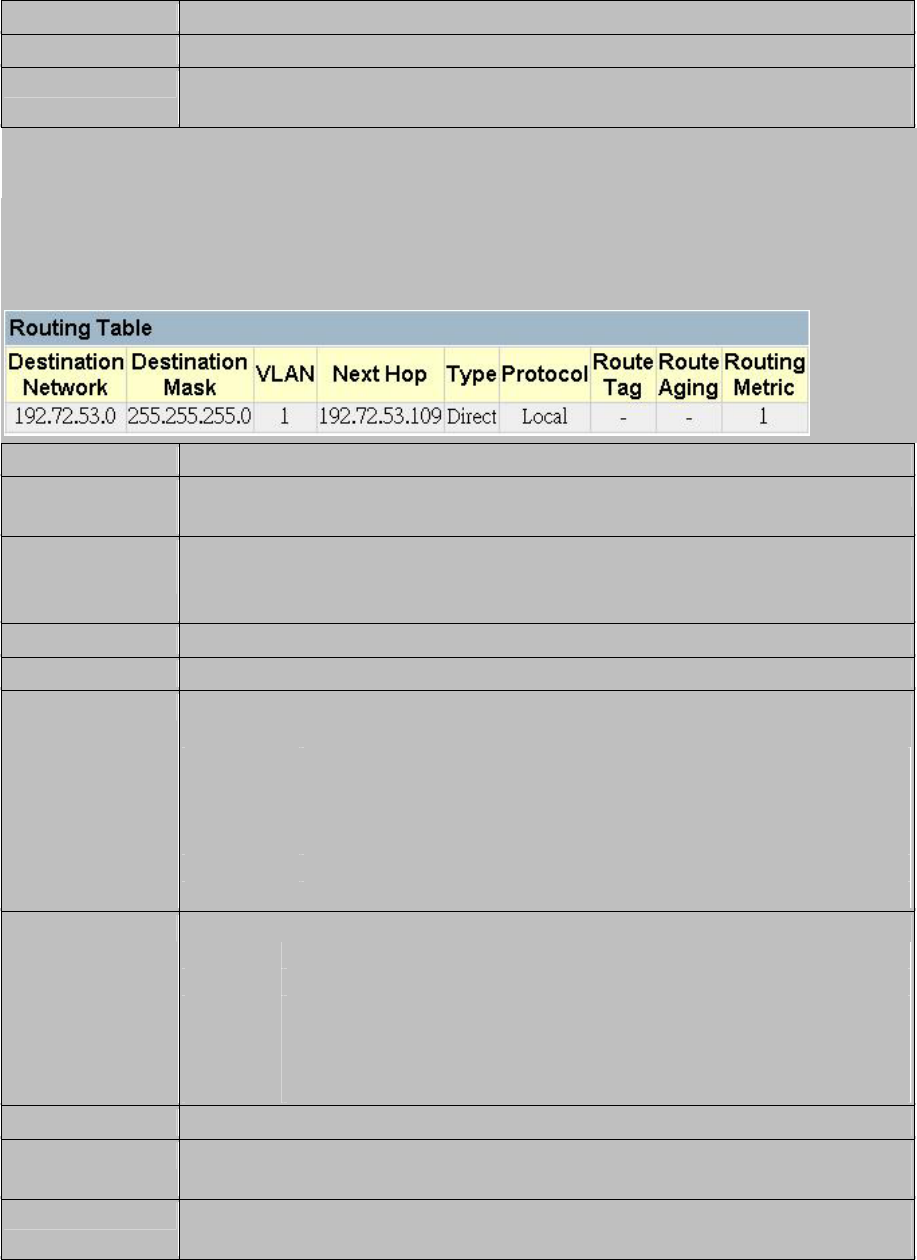
3.7.6.3.Routing Table
The Routing Table lists the routes through which all recognized Ethernet networks (and
corresponding VLANs) can be reached. This table includes all routes learned through
routing protocols or manual configuration.
Parameter Description
Destination
Network
A destination network, subnet or host.
Destination
Mask
The subnet mask that specifies the bits to match. A routing entry will
be used for a packet if the bits in the address set by the destination
mask match the Destination Network.
VLAN The VLAN within which the gateway or destination address resides.
Next Hop The IP address of the router at the next hop.
Type The IP route type for the destination network. This switch supports the
following types:
Direct: A directly connected subnetwork.
Indirect: A remote IP subnetwork or host address.
Myself: A switch IP address on a specific IP subnetwork.
Bcast: A subnetwork broadcast address.
Mcast: An IP multicast address.
Invalid: A illegal IP address to be filtered.
Protocol The route was learned in one of the following ways:
Local: Manually configured
Mgmt. : Set via SNMP
ICMP: Obtained via ICMP redirect.
RIP: Learned via RIP protocol.
OSPF: Learned via OSPF protocol.
Other: Learned by some other method.
Route Tag The route tag represents the device that originated this routing entry.
Route Aging The number of seconds elapsed since this route was last updated or
otherwise determined to be correct. (This entry only applies to RIP.)
Routing Metric A relative measure of the path cost from this switch to the destination
network. (This value depends on the specific routing protocol.)


















