User Manual
Hipulse - Single Phase ‘1+N’ UPS System 130 kVA - 110V
1
CHAPTER 1
General Description
1.1 Introduction
The Hipulse Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) System is connected between a
critical load, such as a computer, and its three phase mains power supply. Being
designed to furnish a well regulated 1 phase output power supply under all rated load
and input supply conditions, the system offers the user the following advantages:
Increased power quality:
The UPS has its own internal voltage and frequency regulators which ensure that its
output is maintained within close tolerances independent of voltage and frequency
variations on the mains power lines.
Increased noise rejection:
By rectifying the input a.c. power to d.c. power, and then converting it back to a.c.,
any electrical noise present on the input mains supply line is effectively isolated from
the UPS output, therefore the critical load sees only clean power.
Power blackout protection:
If the mains power fails, the UPS continues to power the critical load from its battery
source, leaving the load immune from power disturbances.
1.2 Design Concept
1.2.1 Hipulse Module Design
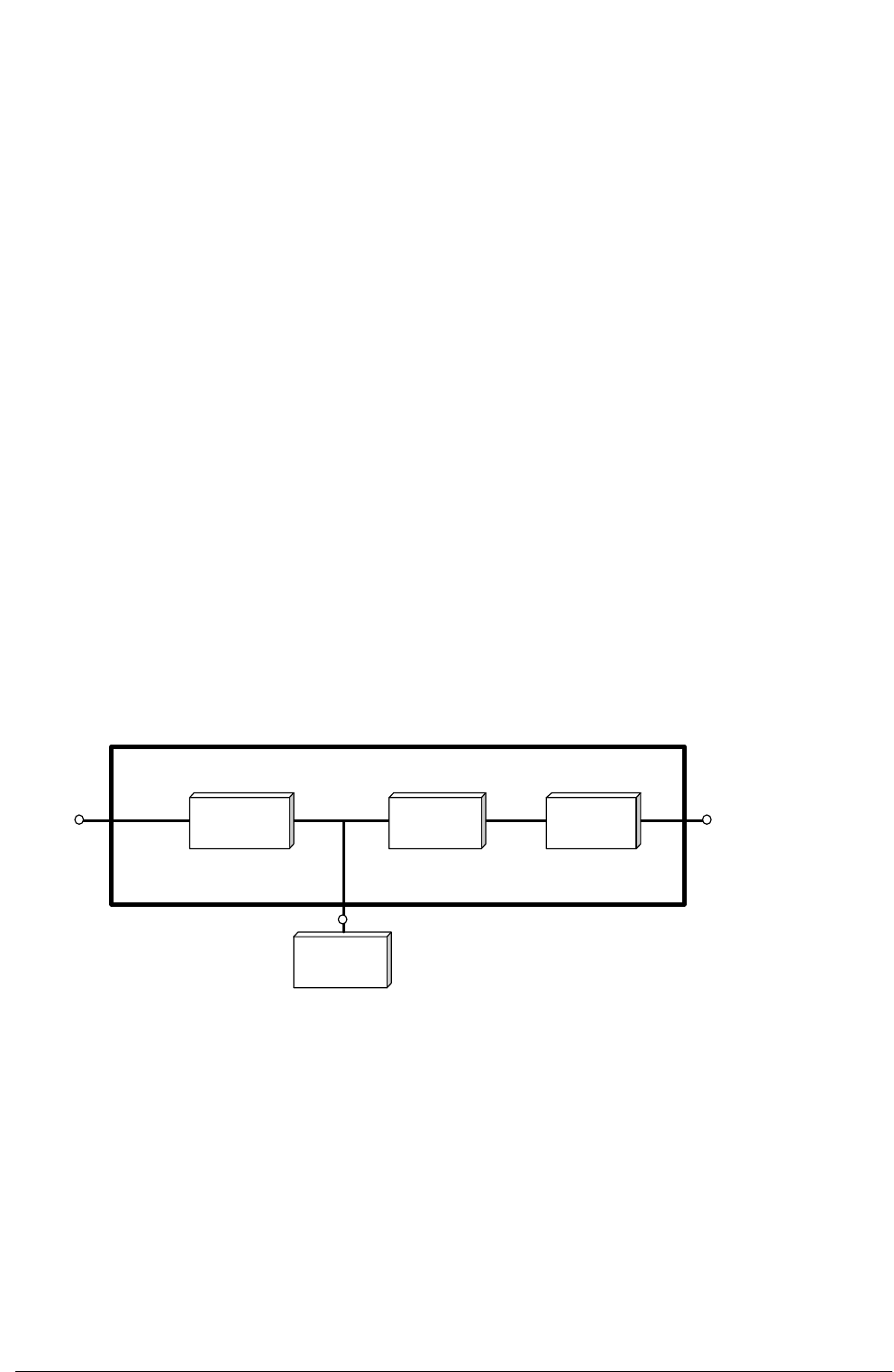
This section describes an individual module's operating principles. The UPS basically
operates as an a.c. - d.c. - a.c. converter (see figure 1 -1 ). This first conversion stage
(from a.c. to d.c.) uses a 3 phase, fully-controlled SCR bridge rectifier to convert the
incoming mains supply into a regulated d.c. busbar.
The d.c. busbar produced by the rectifier provides both battery charging power -
being equipped with a temperature compensated battery charging system, to prolong
battery life - and power to the inverter section - which utilizes the latest IGBT switching
pulse width modulation (PWM) design - and provides the second conversion phase,
i.e. reconverting the d.c. busbar voltage back into an a.c. voltage waveform.
Fig 1-1 : Single Module block diagram
RECTIFIER
STATIC
SWITCH
INVERTER
BATTERY
Mains
Supply
UPS
Output
Supply
(a.c.) (d.c.) (a.c.)
(d.c.)


















