© National Instruments Corporation 15 NI 6509 User Guide and Specifications
Also, make sure the pull-up resistor value is not so large that leakage
current from the DIO line brings the voltage at the resistor below a
TTL-high level of 2 V.
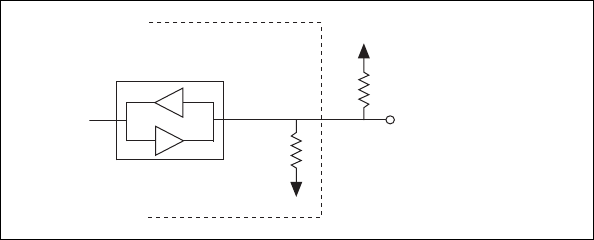
Figure 10. DIO Channel Configured for Low DIO State with External Load
Example:
The switch is set in the low DIO state, which means all DIO lines are pulled
low. If you want to pull one channel high, complete the following steps:
1. Install a load (R
L
). Remember that the smaller the resistance, the
greater the current consumption and the lower the voltage (V).
2. Using the following formula, calculate the largest possible load to
maintain a logic high level of 2 V and supply the maximum sink
current (I).
V = I * R
L
⇒ R
L
= V / I
where:
V = 5 V – 2 V = 3 V is the voltage across R
L
I = 91 μA is the maximum leakage current to the device at high
input
therefore:
R
L
= 33 kΩ is the 3 V / 91 μA
This resistor value, 33 kΩ, provides a minimum of 2 V on the DIO line. You
can substitute smaller resistor values, but they draw more current, leaving
less sink current for other circuitry connected to this line.
Increasing Current Drive on NI USB-6509 Devices
Based on the USB specification, the maximum current that a bus-powered
USB device can draw is limited to 500 mA. Consequently, when the
NI USB-6509 is powered only from a USB port, the current drive capacity
at output channels is limited.
NI USB-6509
Digital I/O Line
+5 V
GND
100 kΩ
R
L
Transceiver


















