HS1100 Wireless Hotspot Gateway User Manual
201
Appendix H. Session Limit and Session Log
Session Limit
To prevent ill-behaved clients or malicious software from using up the system’s connection resources, the
administrator can restrict the number of concurrent sessions that a user can establish.
¾ The maximum number of concurrent sessions (TCP and UDP) for each user can be specified in the Global
policy, which applies to authenticated users, users on a non-authenticated port, privileged users, and
clients in DMZ zones.
¾ When the number of a user’s sessions reaches the session limit (a choice of Unlimited, 10, 25, 50, 100,
200, 350 and 500), the user will be implicitly suspended upon receipt of any new connection request. In
this case, a record will be logged to a Syslog server.
¾ Since this basic protection mechanism may not be able to protect the system from all malicious DoS
attacks, it is strongly recommended to build some immune capabilities (such as IDS or IPS solutions) in
network deployment to maintain network operation.
Session Log
The system can record connection details of each user accessing the Internet. In addition, the log data can be
sent out to a specified Syslog Server, Email Box or FTP Server based on pre-defined interval time.
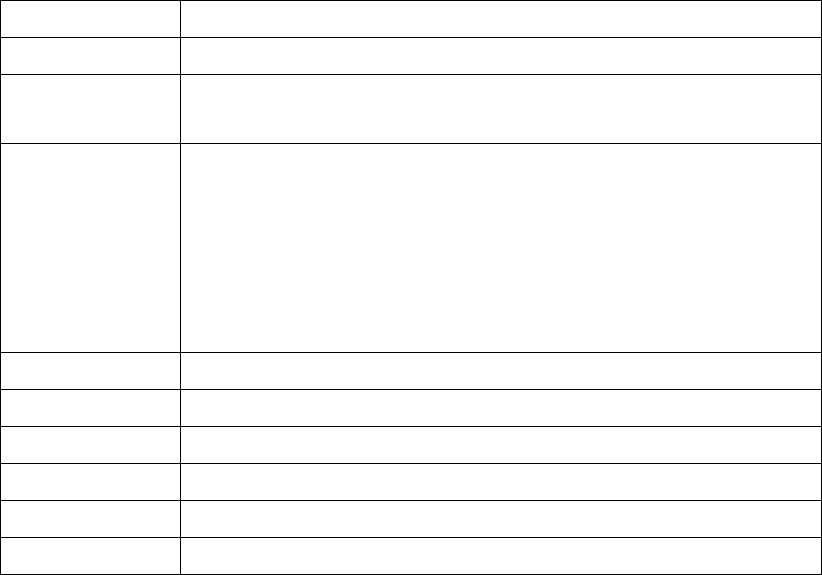
¾ The description of the fields of a session log record is shown as below:
Field Description
Date and Time The date and time that the session is established
Session Type
[New]: This is a newly established session.
[Blocked]: This session is blocked by a Firewall rule.
Username
The account name (with postfix) of the user. When it shows “N.A.”, it
indicates that the user or device does not need to log in with a
username, for example, the user or device is on a non-authenticated
port or on the privileged MAC/IP list. Change the account name
accordingly, if the name is not identifiable in the record.
Note: Only 31 characters are allowed for the combination of
Session Type plus Username.
Protocol The communication protocol of session: TCP or UDP
MAC The MAC address of the user’s computer or device
SIP The source IP address of the user’s computer or device
SPort The source port number of the user’s computer or device
DIP The destination IP address of the user’s computer or device
DPort The destination port number of the user’s computer or device