44 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
2.5.14 Single IP
The NP2624M switch provides a new management tool for a user to manage a group of LAN
switches by an IP agent method. “Single IP” is the name, meaning that the administrator can access
other network devices through one single IP device. There are two management modes: “Agent
mode” and “Stacking mode”.
Unlike a router’s NAT (from virtual IP domain to real IP domain), single IP provides a reverse
access (from real IP domain to virtual IP domain) using an IP-forwarding technology. With this IP-
agent method, the network administrator can remotely control his far-side hosts without being there,
accessing the private domain hosts through the agency of one real IP switch with a “Single IP”.
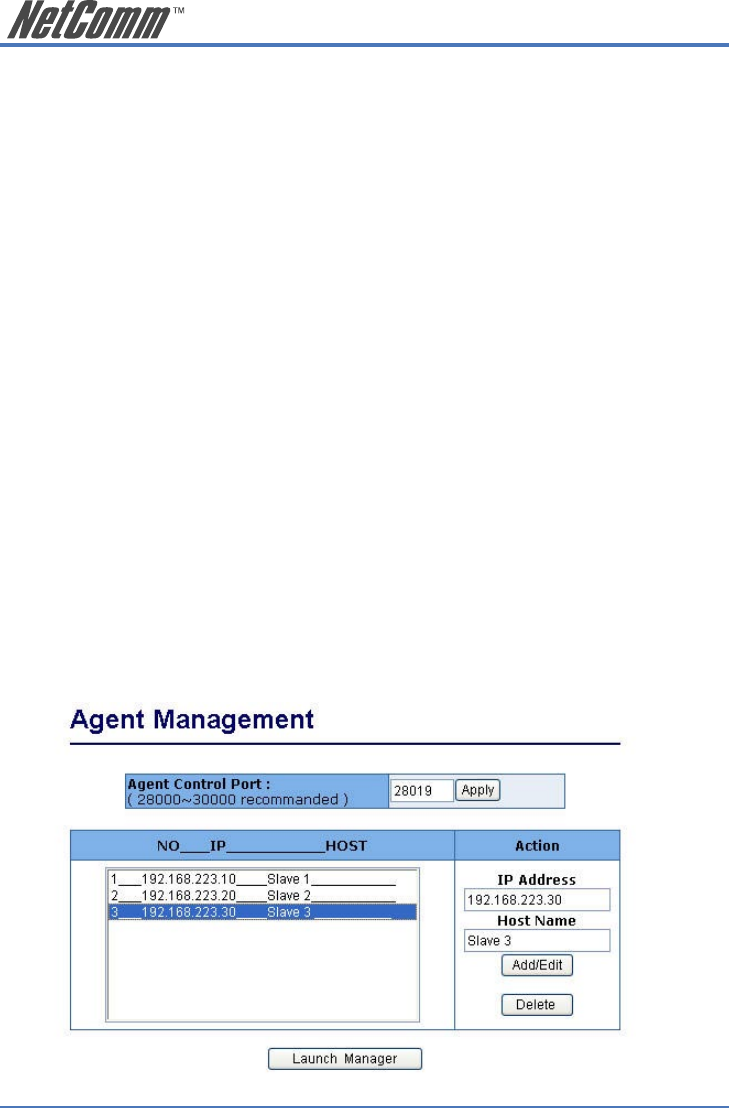
A maximum of 32 sets of information of network devices can be stored in the single IP switch and
16 sets in a stacking switch. Basically these network devices should provide http:// or telnet service
for the single IP switch to forward those protocol packets; meanwhile SNMP protocol can be also
passed through if they support SNMP service.
Moreover, this single IP switch has no exclusiveness, meaning that administrator can group
up network devices of any type (router, switch, server...) or brand without worrying their
incompatibility.
However, for stacking switch, only the switches of the same model can detect each other and
transfer information to their partner, so it won’t support other network devices in this instance. This
is the major difference between single IP agent mode and stacking mode. Please read Chapter 5 for
more information.
Web UIs of “Agent Management” and “Stacking Management” look similar. In these pages, users
can add or delete managed network devices. If the user disables the IP agent function, that is, sets
the management mode to “Agent Slave” or “Stacking Slave” in the IP setting webpage, this item
will not show up in the main menu.
2.5.14.1 Agent Management


















