Calculations 375
MG 1000B Core and MG 1000B Expander requirements
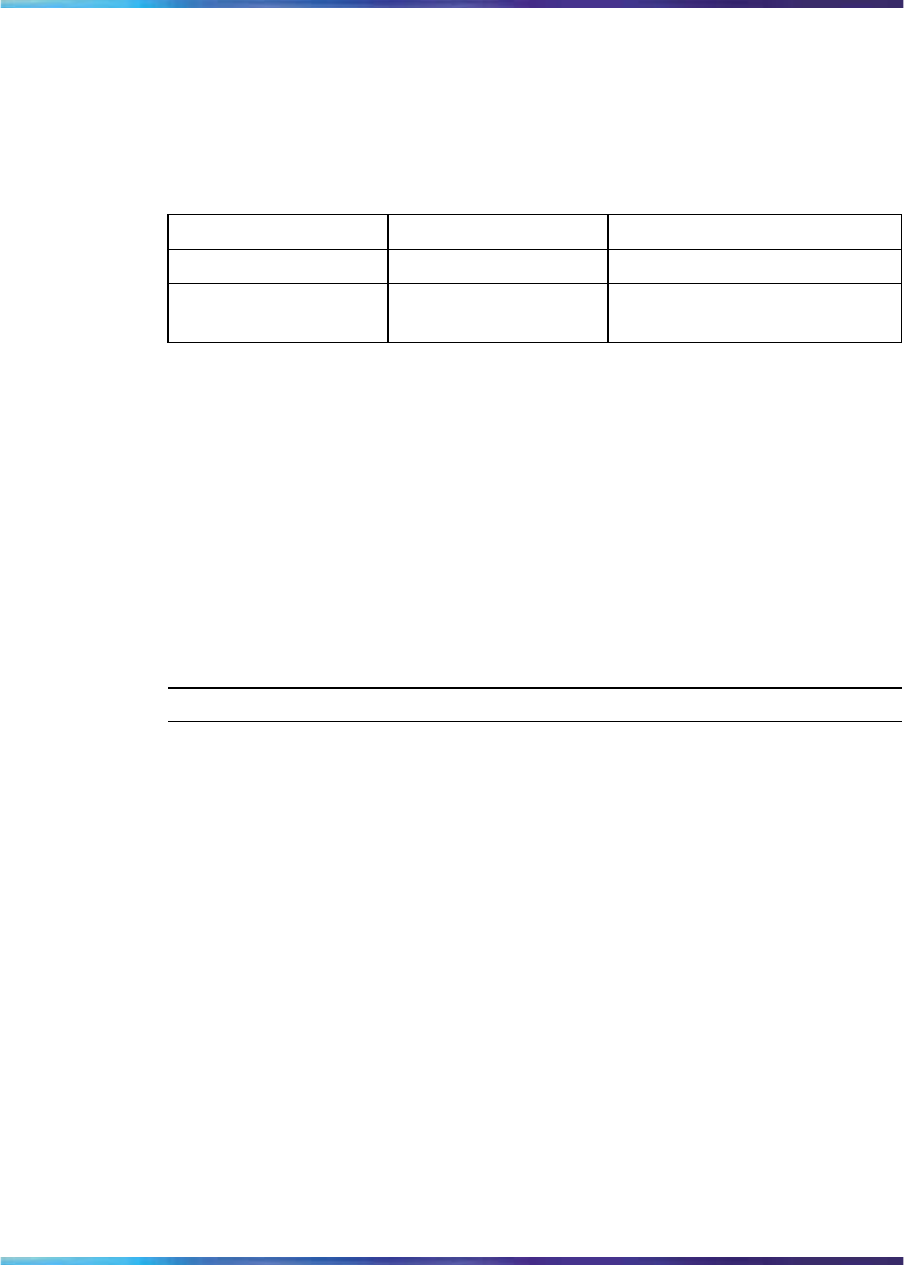
Table 41 "MG 1000B Core and MG 1000B Expander card type, number and
devices" (page 375) shows the number of cards required and the devices
on those cards.
Table 41
MG 1000B Core and MG 1000B Expander card type, number and devices
Card type
Number of cards Devices on cards
MC
1
32 DSP channels
XALC
3
36 Analog (500/2500-type)
telephones
One MG 1000B Core has four slots available, and an MG 1000B Expander
is required for additional cards.
Requirement: one MG 1000B Core
An Analog Line card or Digital Line card has 16 ports. If 36 digital
telephones are used instead of 36 analog (500/2500-type) telephones, the
resulting calculation would yield the same number of cards: three XDLC
cards, taking the place of three XALCs. The total number of card slots and
MG 1000B Core requirements are the same.
Procedure 48
Calculating Call Server Loading
Step Action
Only the CCS from one terminating end of a connection is used in the
Call Server loading calculation. For example, a call from one IP Phone to
another includes the CCS from both telephones. The Call Server loading
calculation divides the CCS by two.
1
Calculate the IP Phone to IP Phone calls:
IT to IT CCS x 100 seconds ÷ average hold time ÷ 2 = IT to IT calls
360 x 100 ÷ 120 ÷ 2 = 150 calls
Dividing by 2 is only required for IT-to-IT traffic. Intra-IT CCS is
double counted in relation to the number of calls. For example, one
call lasting 100 seconds appears as one CCS on the originating
telephone, one call on the CPU, and one CCS on the terminating
telephone. Two CCS on telephones must be divided by two to get
the correct number of calls.
2
Calculate the IP Phone to main office resources (MOR) calls:
IT to IT CCS x 100 seconds ÷ average hold time = IT to MOR calls
Nortel Communication Server 1000
Branch Office Installation and Commissioning
NN43001-314 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 20 June 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks
.


















