Modbus Functions
FP Web-Server V2.11
144
12.1 Overview on Modbus-TCP Functions of the FP
Web-Server
General Information on Modbus-TCP
The Modbus-TCP is a standard global communication protocol (IAONA, Modbus-IDA) and is
used to connect the PLC to third-party PLC equipment, SCADA systems, OPC servers, and
Modbus-RTU gateways.
A Modbus-TCP server waits for an incoming connect from a Modbus-TCP client. Hence:
• A Modbus-TCP server (Ethernet) is comparable to a Modbus-RTU slave (serial).
• A Modbus-TCP client (Ethernet) is comparable to a Modbus-RTU master (serial).
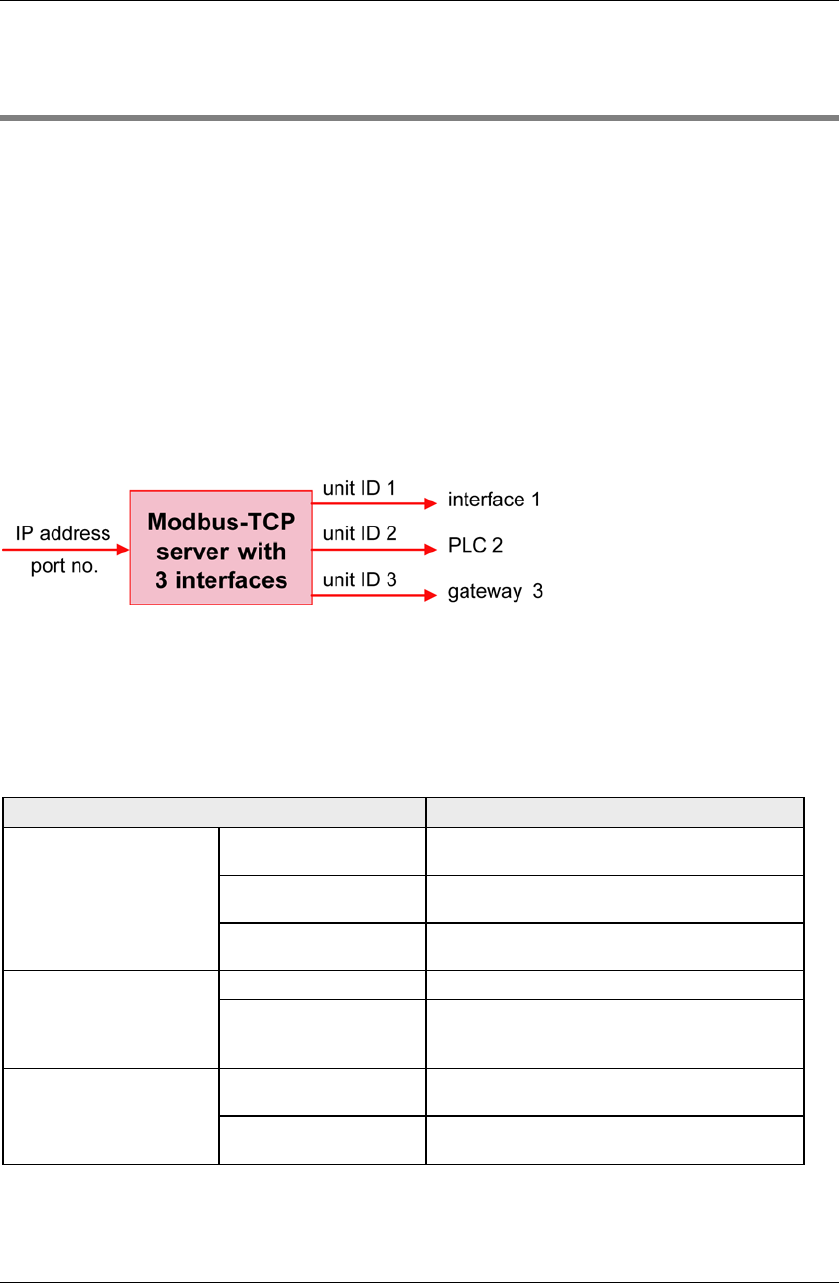
A Modbus-TCP server is addressed with a unique IP address and a port number (default 502).
Using a unit ID address in the Modbus-TCP data packet, various interfaces of the Modbus-TCP
server can be addressed. The unit ID is comparable to the slave address in Modbus-RTU
communication.
Modbus communication is based on a number of specified function codes which can address
different data types. Which function codes and data types are supported depends on the unit
implementation.
FP Web-Server Specific Implementation
The FP WEB Configurator Tool Version 2.1 allows you to configure the FP Web-Server (as an
interface to the PLC) with the following Modbus-TCP server and client functions.
Function Comment
A1 Modbus-TCP Server
Modbus-TCP Client → FP Web-Server → PLC (see
note 2)
A2 Modbus-TCP Server
Modbus-TCP Client → FP Web-Server → multiple
PLCs (see note 1 and note 2)
A
Modbus-TCP Server
(see page
146)
A3 Modbus-TCP Server
Gateway
Modbus-TCP Client → FP Web-Server →
Modbus-RTU Slave (see note 1)
B1 Modbus-TCP Client
PLC → FP Web-Server → Modbus-TCP Server
B
Modbus-TCP Client
(see page
148)
B3 Modbus-TCP Client
Gateway
Modbus-RTU Master (see note 1) → FP
Web-Server → Modbus-TCP Server
B2 Modbus-RTU Master
PLC → FP Web-Server → Modbus-RTU Slave (see
note 1)
In addition: Modbus-RTU
functions (for PLCs that do
not support Modbus-RTU
protocol)
B4 Modbus-RTU Slave
Modbus-RTU Master (see note 1) → FP
Web-Server → PLC


















