UPnP
UPnP provides support for communication between control points and devices. The network media, the
TCP/IP protocol suite and HTTP provide basic network connectivity and addressing needed. On top of
these open, standard, Internet based protocols, UPnP defines a set of HTTP servers to handle
discovery, description, control, events, and presentation.
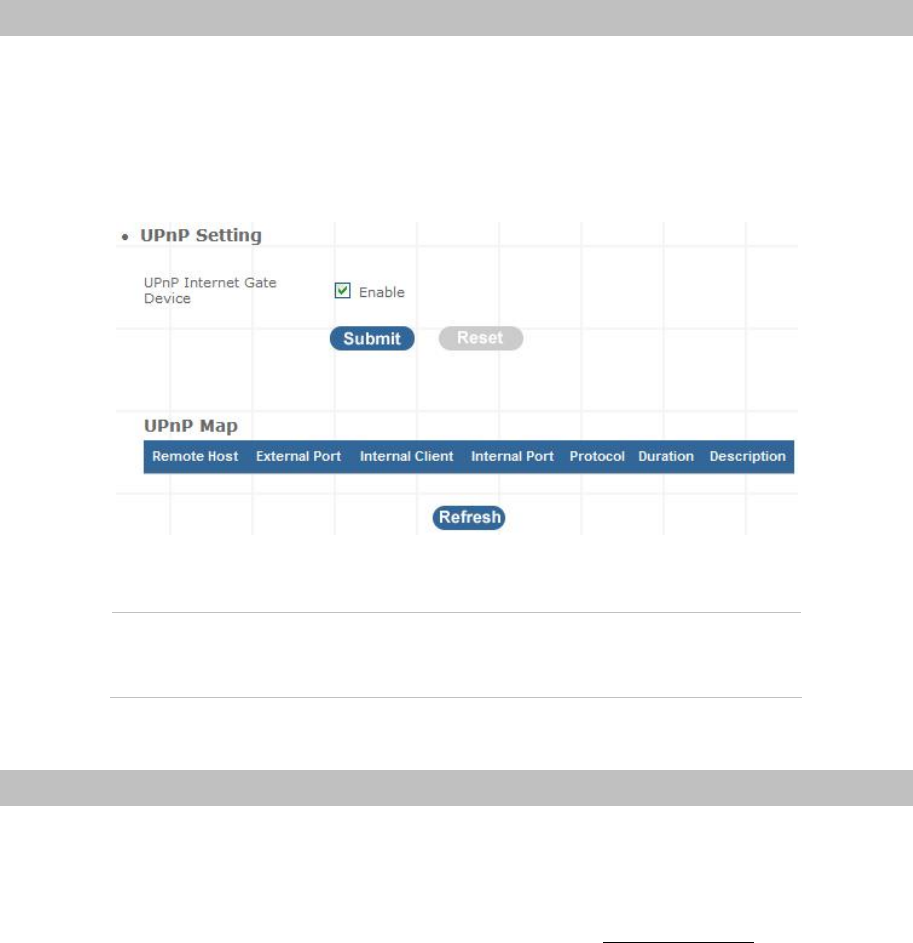
Figure 4-20. UPnP settings
UPNP Internet Gate
Device
Enable/Disable UPNP Service to working, default
setting is Disable.
Table 4-18. UPnP description
DDNS
The DDNS (Dynamic DNS) service allows you to alias a dynamic IP address to a static hostname,
allowing your computer to be more easily accessed from various locations on the Internet. Without
DDNS, the users should use the WAN IP to reach internal server. It is inconvenient for the users if this
IP is dynamic. With DDNS supported, you apply a DNS name (e.g., www.IPPBX.com
) for your server
(e.g., Web server) from a DDNS server. The outside users can always access the web server using the
www.IP-PBX.com regardless of the WAN IP.
When you want your internal server to be accessed by using DNS name rather than using the dynamic
IP address, you can use the DDNS service. The DDNS server allows to alias a dynamic IP address to a
static hostname.
Unlike DNS that only works with static IP addresses, DDNS works with dynamic IP addresses, such as
those assigned by an ISP or other DHCP server. DDNS is popular with home networkers, who typically
receive dynamic, frequently-changing IP addresses from their service provider.
54
DDNS is a method of keeping a domain name linked to a changing (dynamic) IP address. With most
Cable and DSL connections, you are assigned a dynamic IP address and that address is used only for
the duration of that specific connection. With the IP-PBX, you can setup your DDNS service and the
IP-PBX will automatically update your DDNS server every time it receives a different IP address.


















