Hard Disk Management = 87
Hard Disk Management
This Image Servers employ an advanced Serial-ATA controller that manages four high-
capacity hard disks operating in a RAID-5 configuration. This design increases system
performance, and by storing parity data, helps prevent data loss should a drive fail.
The Image Server brings a high level of reliability to Serial-ATA RAID through a new,
switched architecture that exceeds the reliability of SCSI shared-bus storage systems. The earlier
shared-bus architecture of SCSI has inherent performance limitations due to arbitration latency,
since only one drive may use the bus at a time. Further, a single drive failure can bring the entire
storage system down.
By contrast, the Image Server uses a non-blocking switched architecture to isolate the drives
from one another. Any drive failure makes that drive unavailable and the rest of the storage system
remains undisturbed. In addition, the Image Server uses Advanced Data Protection features, where
all drive commands are checked to ensure that no command corruption has taken place over the
entire data path.
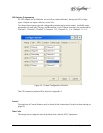
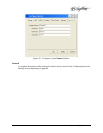
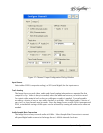
Some of the Image Server RAID implementation features and benefits include:
• Non-blocking switch technology with RAID 5 parity
• On-board processor minimizes host CPU overhead
• Easy-to-configure arrays
• Dynamic sector repair for robust data protection
• Accelerated RAID-5 writes
About RAID 5
A RAID 5 configuration features the data striping of RAID 0 combined with the parity benefits of
RAID 4. Using a simple parity (exclusive OR) function, RAID 5 can tolerate the loss of one drive.
Parity information is distributed across all drives rather than being concentrated on a single disk.
This avoids throughput loss due to contention for the parity drive. Spare drives can be used to
rebuild a failed array.
RAID-5 capacity equals the size of drive times (number of drives -1). In addition, the array’s
storage efficiency increases with the number of disks; from 66.7 % for 3 drives to 75 % for 4
drives: storage efficiency = (number of drives -1) X (number of drives).