75
6 F 3 B 0 3 6 2
f. When the TCP socket interface is used, transmitted data is divided (fragmented) into units of a
size determined when the connection between the two sockets was established. The upper
limit of the fragment size is 1460 bytes. This is the limit of the length of packets (data units
flowing on the network) transmitted over the network. (See figure 6.8.)
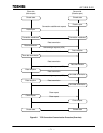
For example, when transmitting a 2000 byte data set, which is the largest data size that can be
handled by the Ethernet Port, the phenomenon shown in figure 6.7 can occur. The largest
segment size that can be received in this case is 1460 bytes.
¬ The sending T2N user program requests a transmission of 2000 bytes.
- The transmitted data is divided into two units called segments, A (with 1460 bytes) and
B (with 540 bytes) by the send side Ethernet Port.
® A and B are put onto the network in order.
¯ The data that arrived at the receive side Ethernet Port is acquired by a receive request for
2000 bytes from the T2N, and stored in the user specified register area. (See section 6.3
(7).)
The amount of data that can be acquired by a TCP receive request differs depending on
the timing with which the T2N issues the receive request and the timing with which the
data arrives at the Ethernet Port.
• If data has not yet arrived at the receive side Ethernet Port when the receive request is
issued:
→ When segment A arrives at the Ethernet Port, only segment A will be passed to
the requester.
• If only segment A has arrived at the receive side Ethernet Port when the receive
request is issued:
→ Only segment A will be passed to the requester.
• If segments A and B have arrived at the receive side Ethernet Port when the receive
request is issued:
→ A data item consisting of A and B will be passed to the requester.
° If B was not received, another receive request can be issued from the T2N to acquire B.