Parameters Parameter Types. The following table contains explanations and examples
of the parameter types you might see later in this chapter.
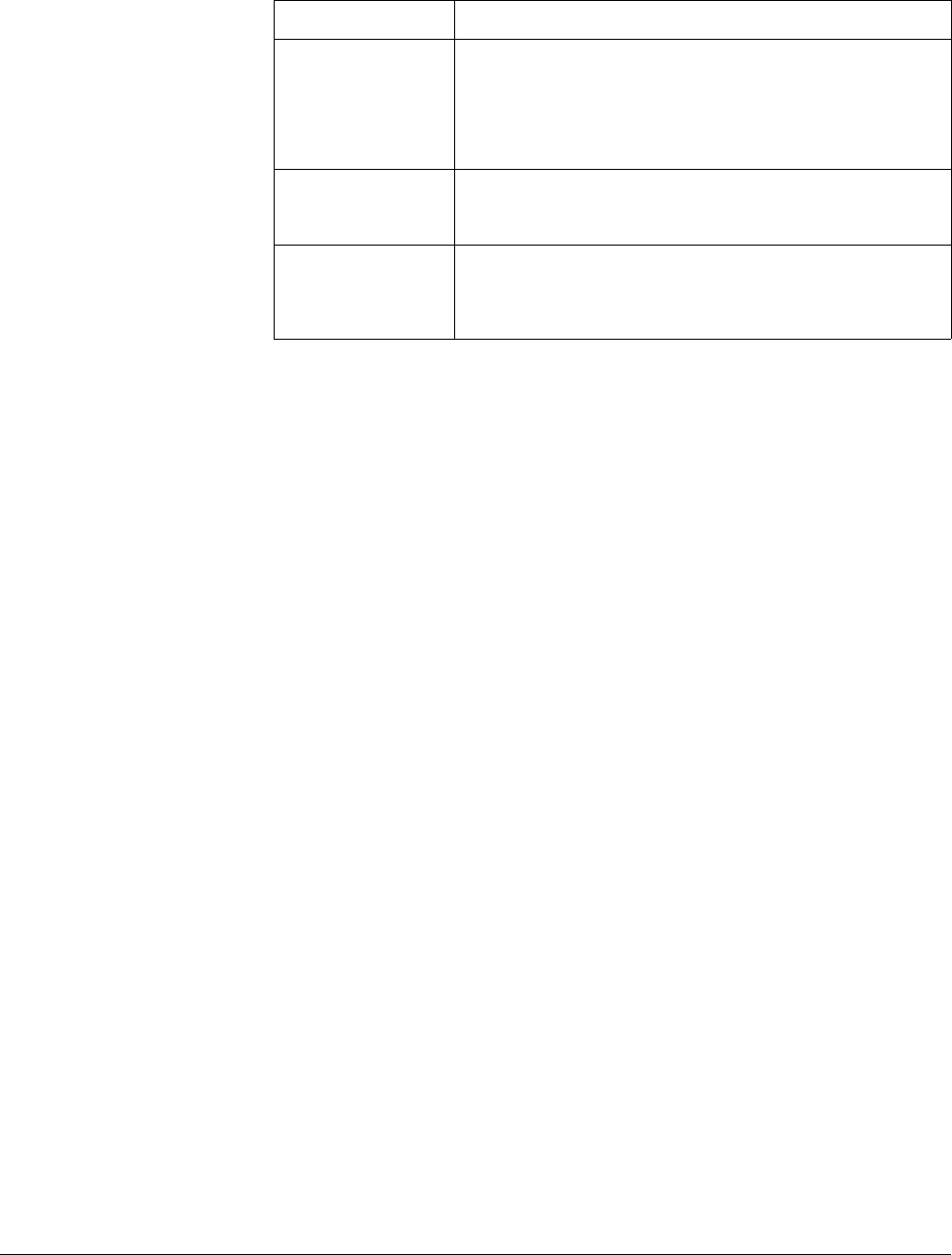
Table 5-1. SCPI Parameter Types
Parameter Type Explanations and Examples
Numeric Accepts all commonly used decimal representations of
numbers including optional signs, decimal points, and
scientific notation.
123, 123E2, -123,-1.23E2, .123, 1.23E-2, 1.23000E-01.
Special cases include MIN, MAX and INF.
Boolean Represents a single binary condition that is either true or false.
ON, OFF, 1, 0.
Discrete Selects from a finite set of values. These parameters use
mnemonics to represent each valid setting. An example is
TRIGger:SOURce <source> where <source> can be BUS,
EXT, HOLD, or IMM.
Optional Parameters. Parameters shown within square brackets ([ ]) are
optional parameters. (Note that the brackets are not part of the command
and are not sent to the instrument.) If you do not specify a value for an
optional parameter, the instrument chooses a default value.
For example, consider the ARM:COUNt? [ MIN | MAX ] command. If
you send the command without specifying a parameter, the present
ARM:COUNt value is returned. If you send the MIN parameter, the
command returns the minimum count available. If you send the MAX
parameter, the command returns the maximum count available. Be sure to
place a space between the command and the parameter.
Linking Commands Linking IEEE 488.2 Common Commands with SCPI Commands: Use a
semicolon between the commands. For example:
*RST;OUTP ON or TRIG:SOUR HOLD;*RST
Linking Multiple SCPI Commands: Use both a semicolon (;) and a colon
(:) between the commands. For example:
ARM:COUN 1;:TRIG:SOUR EXT
Chapter 5 Agilent E1364A Form C Switch Command Reference 43


















