40
4.5.2 Static Route
Static routing is the simplest form of network routing. It makes available
to a switch/router to forward packets from predetermined ports through
a predictable path into and out of a network. Static routing is solid, but
does not address to the fluctuation in the network, therefore, it might
result in destination net unreachable.
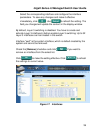
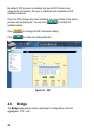
To create a static route entry, you have to configure the following
information:
Destination: Input destination IP address.
Netmask: Input subnet mask of the destination.
Gateway: Input gateway IP address.
Metric: Metric/cost for the destination (1-15).
Static routing is easy to set up and be managed particularly in small
networks. But, it needs additional planning and management in
advanced. Meanwhile, it does not scale well in large networks.
If a match is not found in the routing table for the destination IP address,
then a default route is required. A default route is somewhile called the
"route of last resort". It is the last route tried when all other routes fail.
Since routing has longest prefix match behavior, the default route has
the fewest number of network bits matching and is therefore less
specific. A default route is always configured with both 'Destination' and
'Netmask' as the value of '0.0.0.0'.
Click on
when you add a new static route and you will see
the new added entry shows in the list. You can remove the existed route
by clicking the button, then clicking on
. The route added and
removed will be saved in configuration file immediately.
Click
to make the setting effective. Click to refresh
the settings to current value.