Chapter 1 Overview
14 Avaya M770 M-ACCF/SF ATM Access Modules User’s Guide
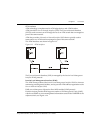
LAN Emulation Address Resolution Protocol (LE_ARP)
An LE_ARP request is sent to the LES to locate the destination MAC address. The
LES in turn sends the LE_ARP request to all of the LECs in the Emulated LAN.
LECs represent (act as a proxy for) MAC address devices connected to the Ethernet
ports. When a LEC receives an LE_ARP request it checks whether the MAC address
is on its Switch. It does this by checking the entries in the Switch database.
If the MAC address belongs to one of the devices connected to an Ethernet port, the
LEC sends an LE_ARP response to the LEC that sent the original LE_ARP request.
The LEC that sent the LE_ARP request adds this information to its ARP Table. The
LEC then sets up a direct connection through the ATM network to the appropriate
LEC, so that subsequent frames are forwarded more efficiently.
What Happens to Unicast Frames?
The path a unicast frame takes through the ATM network depends on whether the
location of the destination address is known to the sending LEC.
• If the location of the destination address is known, the LEC sets up a direct
connection to the LEC serving the destination address.
• If the location of the destination address is unknown, a unicast frame is sent
to the Broadcast and Unknown Server (BUS); where it is treated in the same way as
a broadcast or multicast frame.
In addition the sending LEC attempts to locate the LEC serving the destination
address. It does this using the LE_ARP process, described in “LAN Emulation
Address Resolution Protocol (LE_ARP)”.
What Happens to Broadcast and Multicast Frames?
Each Emulated LAN (ELAN) acts as a broadcast domain. When a broadcast or
multicast frame is passed to the LEC for transmission, the frame is sent to the
Broadcast and Unknown Server (BUS).
When the LEC receives a broadcast, multicast, or unicast frame it checks to see if it
originally sent the frame, and then does the following:
• If the LEC sent the frame, it discards the frame.
• If the LEC did not send the frame, the LEC passes the frame to the Ethernet
device so that it can be forwarded to the appropriate port(s)
Note: Unlike broadcast and multicast frames, the number of unicast frames that can
be sent to the BUS every second is limited so as not to overload the BUS and LECs
with too much traffic.