Chapter 2 Applications
Avaya M770 M-ACCF/SF ATM Access Modules User’s Guide 29
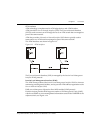
Extending VLANs Through the ATM Network
When setting up VLANs and extending them into the ATM network you should
consider the following (see Figure 1.17):
• What logical network domains, VLANs, do you wish to set up?
Traffic from one Emulated LAN (ELAN) will not be seen on another ELAN
(unless a router is used), as they are logically separate domains. For this reason
you should consider:
— What ELANs you require.
— How the VLANs will map to the ELANs.
— If you need to route between any of your ELANs.
• Will you have sufficient ELAN resources?
When calculating the resources you require, you should consider the number of:
— ELANs that your LAN Emulation services can support.
— VLANs/ELANs that each edge-device can support.
— Virtual circuits required.
— MAC addresses that can be held in the device LAN Emulation ARP Table.
When a LAN Emulation Client (LEC) joins an ELAN, up to five control
connections may be required before any data is transferred over a separate data
connection (VCC). Each time a LEC connects to another LEC a further
connection is required. You should keep this in mind when calculating the
number of connections you require.
The ATM access module provides the following resources:
— Up to 16 LECs to extend VLANs into the ATM network over ELANs.
— 3740 Virtual Circuits to/from the ATM network.
— 8000 remote MAC Addresses.
Note: The ATM access module supports only 16 LECs, but this does not limit your
network to 16 ELANs. You can expand your network by adding additional ATM
access modules to the Avaya M770 Switch or by configuring additional LECS to
other ELANs.
• Are the LAN Emulation services configured correctly?
Is the LAN Emulation service that the LAN Emulation Client (LEC) is going to
join configured correctly?
For example, if your network uses a LAN Emulation Client Server (LECS), does
the LECS know about the LES, and is the LES active? Have you supplied a valid
ELAN name?