Chapter 11 Avaya P330 Layer 2 Features
82 Avaya P334T-ML User’s Guide
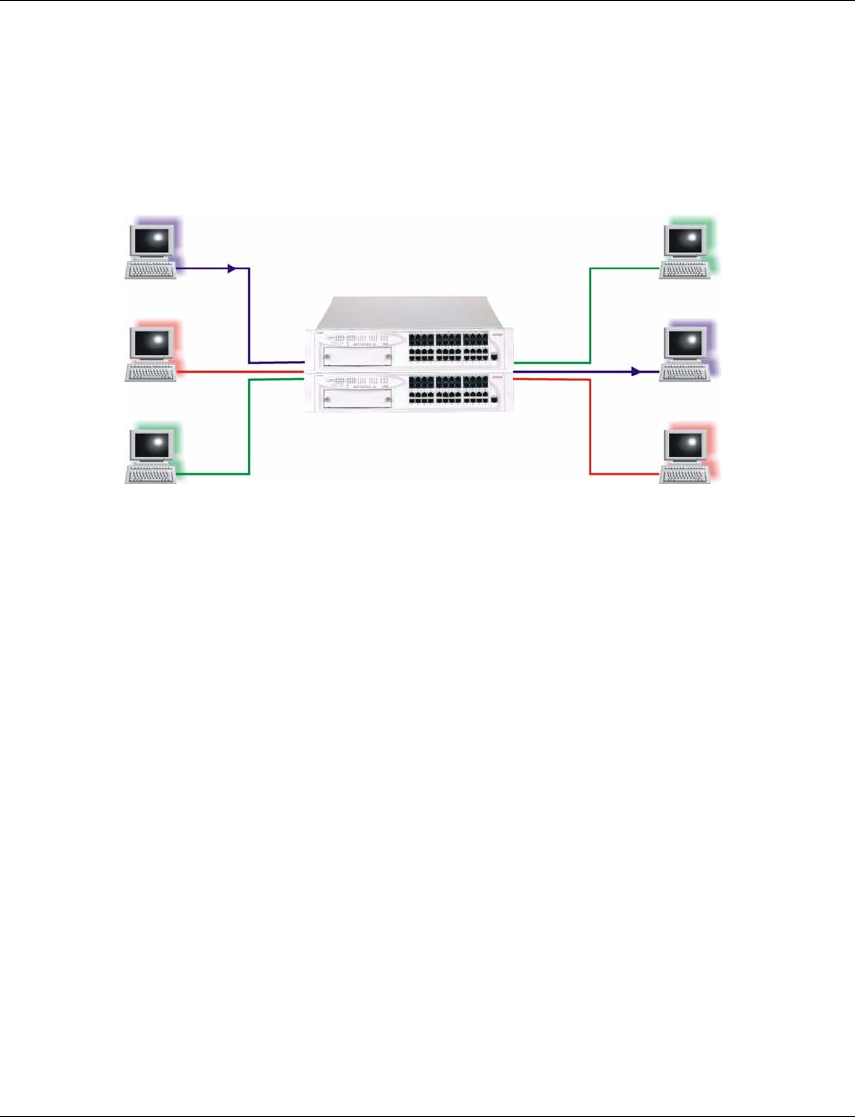
In Figure 11.2, the switch has three separate VLANs: Sales, Engineering, and
Marketing (Mktg). Each VLAN has several physical ports assigned to it with PC’s
connected to those ports. When traffic flows from a PC on the Sales VLAN for
example, that traffic is only forwarded out the other ports assigned to that VLAN.
Thus, the Engineering and Mktg VLANs are not burdened with processing that
traffic.
Figure 11.2 VLAN Switching and Bridging
VLAN Tagging
VLAN Tagging is a method of controlling the distribution of information on the
network. The ports on devices supporting VLAN Tagging are configured with the
following parameters:
•Port VLAN ID
•Tagging Mode
The Port VLAN ID is the number of the VLAN to which the port is assigned.
Untagged frames (and frames tagged with VLAN 0) entering the port are assigned
the port's VLAN ID. Tagged frames are unaffected by the port's VLAN ID.
The Tagging Mode determines the behavior of the port that processes outgoing
frames:
• If Tagging Mode is set to “Clear”, the port transmits frames that belong to the
port's VLAN table. These frames leave the device untagged.
• If Tagging Mode is set to “IEEE-802.1Q”, all frames keep their tags when they
leave the device. Frames that enter the switch without a VLAN tag will be
tagged with the VLAN ID of the port they entered through.
Multi VLAN Binding
Multi VLAN binding (Multiple VLANs per port) allows access to shared resources
by stations that belong to different VLANs through the same port. This is useful in
applications such as multi-tenant networks, where each user has his a VLAN for
Sales
Sales
Mktg
Mktg
Engineering
Engineering


















