724-746-5500 | blackbox.com
Page 21
Chapter 3: Installation
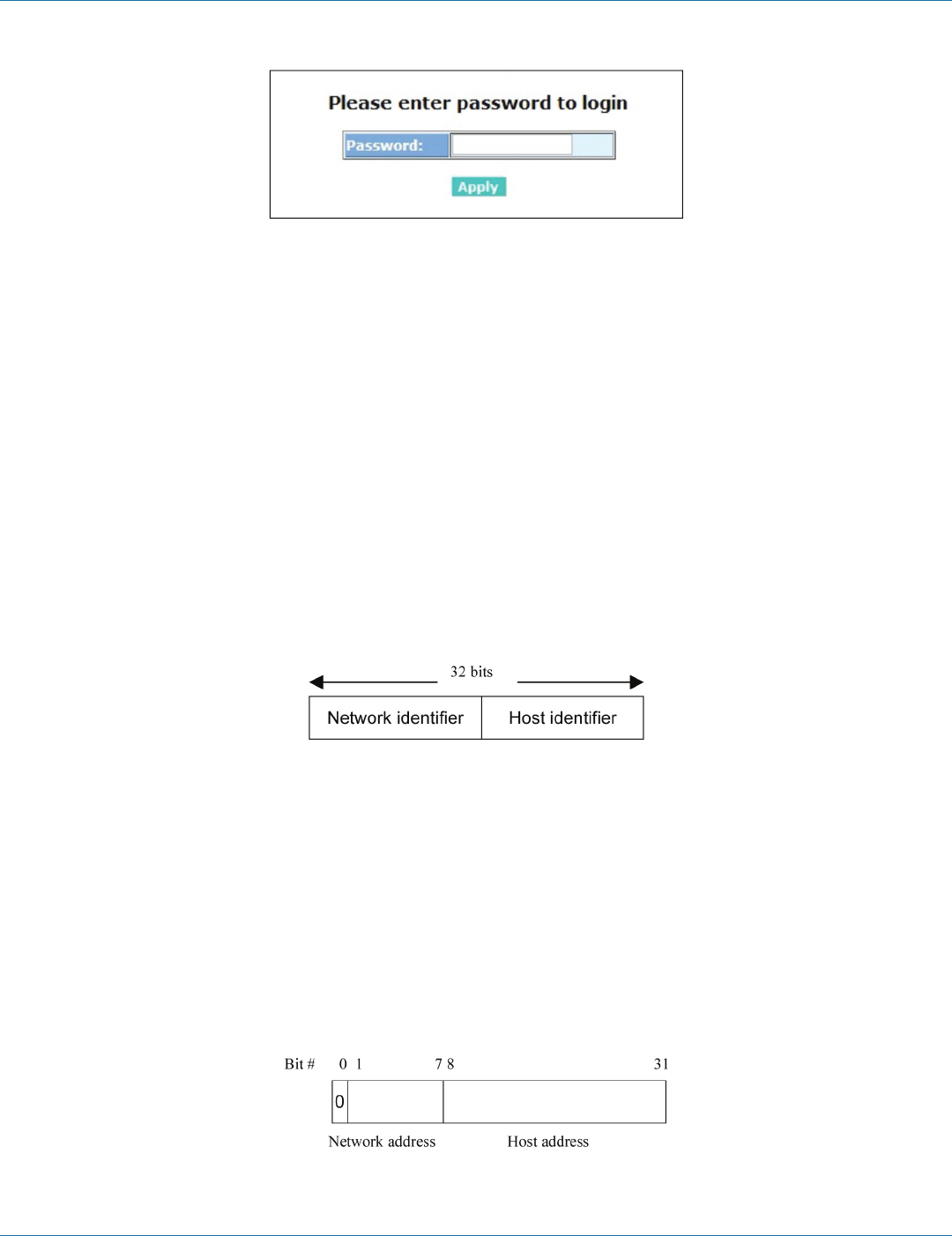
Figure 3-7. The Login screen for the Web.
3.1.4 Address Assignment
For IP address configuration, there are four parameters that need to be filled in. They are IP address, Subnet Mask, Default
Gateway, and DNS.
IP address:
The address of the network device in the network is used for internetworking communication. Its address structure is shown in
Figure 3-8. It is split into predefined address classes or categories.
Each class has its own network range between the network identifier and host identifier in the 32-bit address. Each IP address has
two parts: network identifier (address) and host identifier (address). The network identifier is the network where the addressed
host resides, and the host identifier is the individual host in the network that the address of the host refers to. The host identifier
must be unique in the same LAN. The IP address we use here is version 4, known as IPv4.
Figure 3-8. IP address structure.
The switch divides the IP address into three classes, class A, class B, and class C. The rest of the IP addresses are for multicast and
broadcast. The bit length of the network prefix is the same as that of the subnet mask and is denoted as IP address/X, for
example, 192.168.1.0/10. Each class has its address range (described next).
Class A:
A Class A address is less than 126.255.255.255. The switch can define a total of 126 networks because the address 0.0.0.0 is
reserved for a default route and 127.0.0.0/8 is reserved for a loopback function.
Figure 3-9. Class A IP address.