724-746-5500 | blackbox.com
Page 41
Chapter 4: Basic Concepts and Management
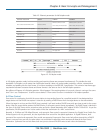
Figure 4-10. Tag format.
VLAN Protocol ID: 8100 is reserved for VLAN-tagged frame.
User Priority: 3 bits long. User priority is defined from 7–0. 0 is the lowest priority.
CFI: Canonical Format Indicator is 1 bit long. It encapsulates a token ring packet so it can travel across the Ethernet. Usually, it is
set to 0.
VLAN ID: 12 bits long. 0 means no VLAN ID is present. 1 means default VLAN, 4095 is reserved.
VLAN-tagged frame: An Ethernet frame, carrying a VLAN tag field, contains VLAN identification without the value of 0 and 4095,
and priority information.
Priority-tagged frame: An Ethernet frame, carrying a VLAN tag field, contains VLAN identification with the value of 0 and priority
information.
Untagged frame: An Ethernet frame carries no VLAN tag information.
VLAN Identifier: Also referred to as VID. It is used to identify whether a member belongs to the VLAN group with the VID. The
assignable number is 1–4094. If VID=0, the tagged frame is a priority packet. Values of 0 and 4095 also cannot be assigned in
VLAN management.
Port VLAN Identifier: VLAN identifier of a port. It also can be referred to as PVID. When an untagged frame or a priority-tagged
frame is received, the frame will be inserted into the PVID of that port in the VLAN tag field. The frame with VID assigned by a
port is called PVID. Each port can only be assigned a PVID. The default value for PVID is 1, the same as VID.
Ingress filtering: The process to check a received packet and compare its VID to the VLAN membership of the ingress port. The
ingress filtering can be set per port. When receiving a packet, a VLAN bridge examines if the VID in the frame’s header presents.
If the VID of the received packet presents, the VID of the packet is used. And VLAN bridge will check its MAC address table to
see if the destination ports are members of the same VLAN. If both are members of the tagged VLAN, then the packet will be
forwarded.
If the packet is an untagged or a null tag packet, the ingress port’s PVID is applied to the packet. A VLAN bridge will then look up
the MAC address table and determine to which ports the packet should be forwarded. Next, it will check to see if the destination
ports belong to the same VLAN with that PVID. If the destination ports are members of the VLAN used by the ingress port, the
packet will be forwarded.
NOTE: VID cannot be 0 or 4095.
Ingress Rule: Each packet received by a VLAN-aware bridge will be classified to a VLAN. The classification rule is described as
follows.
1. If the VID of the packet is null VID (VID=0) or this packet is an untagged packet:
a. If there are still some other ways (for example, protocol, MAC address, application, IP-subnet, etc.) to classify the incoming
packets besides port-based classification, use the value of VID offered by other classifications for a VLAN’s classification.
b. If there is only port-based classification implemented, other classification approaches cannot offer non-zero VID for the
incoming packets, and then assign the PVID to the incoming packets as VID for the classification of the VLAN group.