724-746-5500 | blackbox.com
Page 36
Chapter 4: Basic Concepts and Management
When MAC parses the received frame and finds a reserved special value 0x8100 at the location of the Length/Type field of the
normal non-VLAN frame, it will interpret the received frame as a tagged VLAN frame. If this happens in a switch, the MAC will
forward it, according to its priority and egress rule, to all the ports associated with that VID. If it happens in a network interface
card, MAC will deprive the tag header and process it in the same way as a basic normal frame. For a VLAN-enabled LAN, all
involved devices must be equipped with the optional VLAN function.
At operating speeds above 100 Mbps, the slotTime employed at slower speeds is inadequate to accommodate network
topologies of the desired physical extent. Carrier Extension provides a means by which the slotTime can be increased to a
sufficient value for the desired topologies, without increasing the minFrameSize parameter, because this would have deleterious
effects. Non-data bits, referred to as extension bits, are appended to frames that are less than slotTime bits in length so that the
resulting transmission is at least one slotTime in duration. Carrier Extension can be performed only if the underlying physical layer
is capable of sending and receiving symbols that are readily distinguished from data symbols, as is the case in most physical layers
that use a block encoding/decoding scheme.
The maximum length of the extension is equal to the quantity (slotTime - minFrameSize). The MAC continues to monitor the
medium for collisions while it is transmitting extension bits, and it will treat any collision that occurs after the threshold (slotTime)
as a late collision.
10 Mbps
100 Mbps
100 Mbps
100 Mbps
100 Mbps
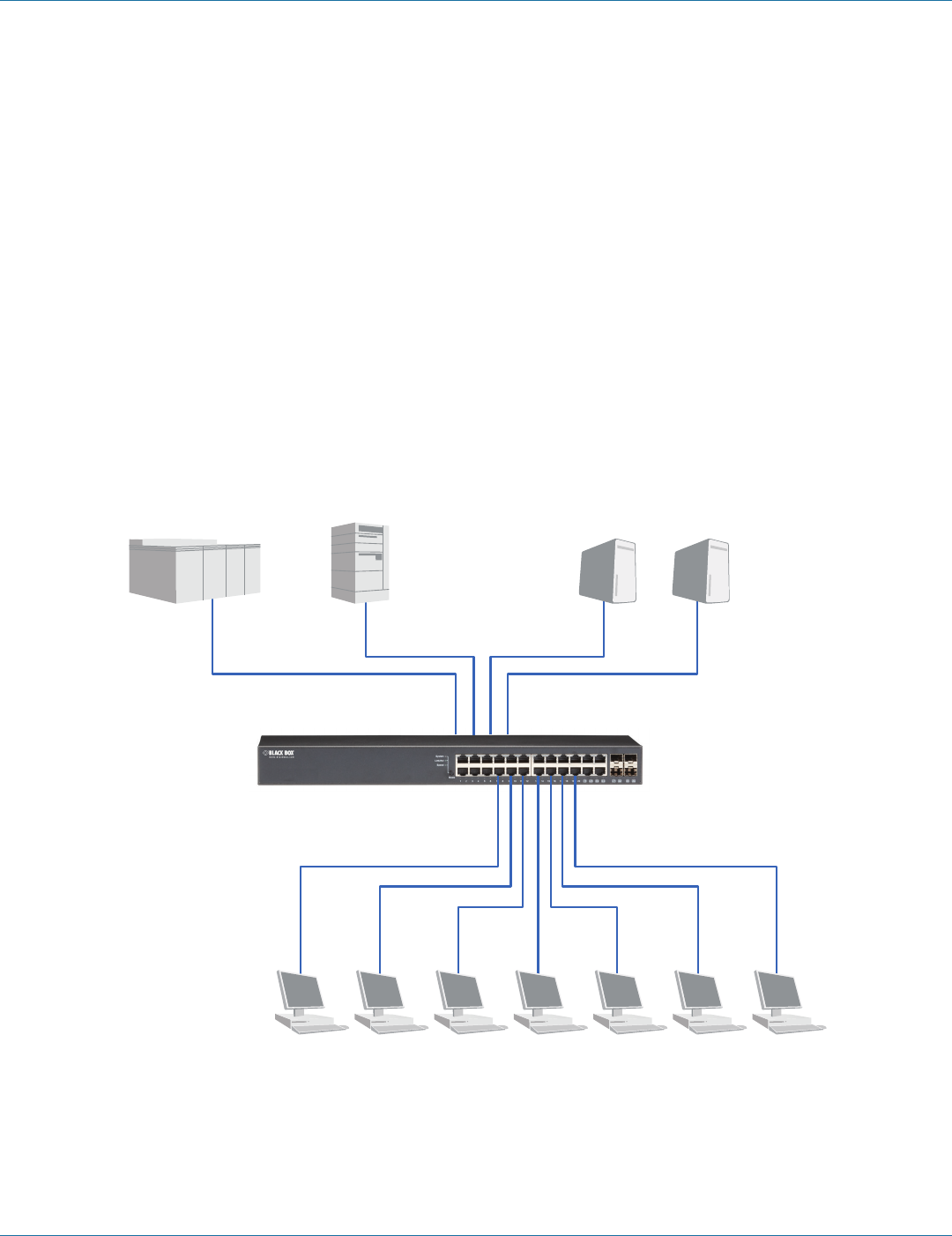
Figure 4-7. Collision domain.