724-746-5500 | blackbox.com
Page 22
Chapter 3: Installation
Class B:
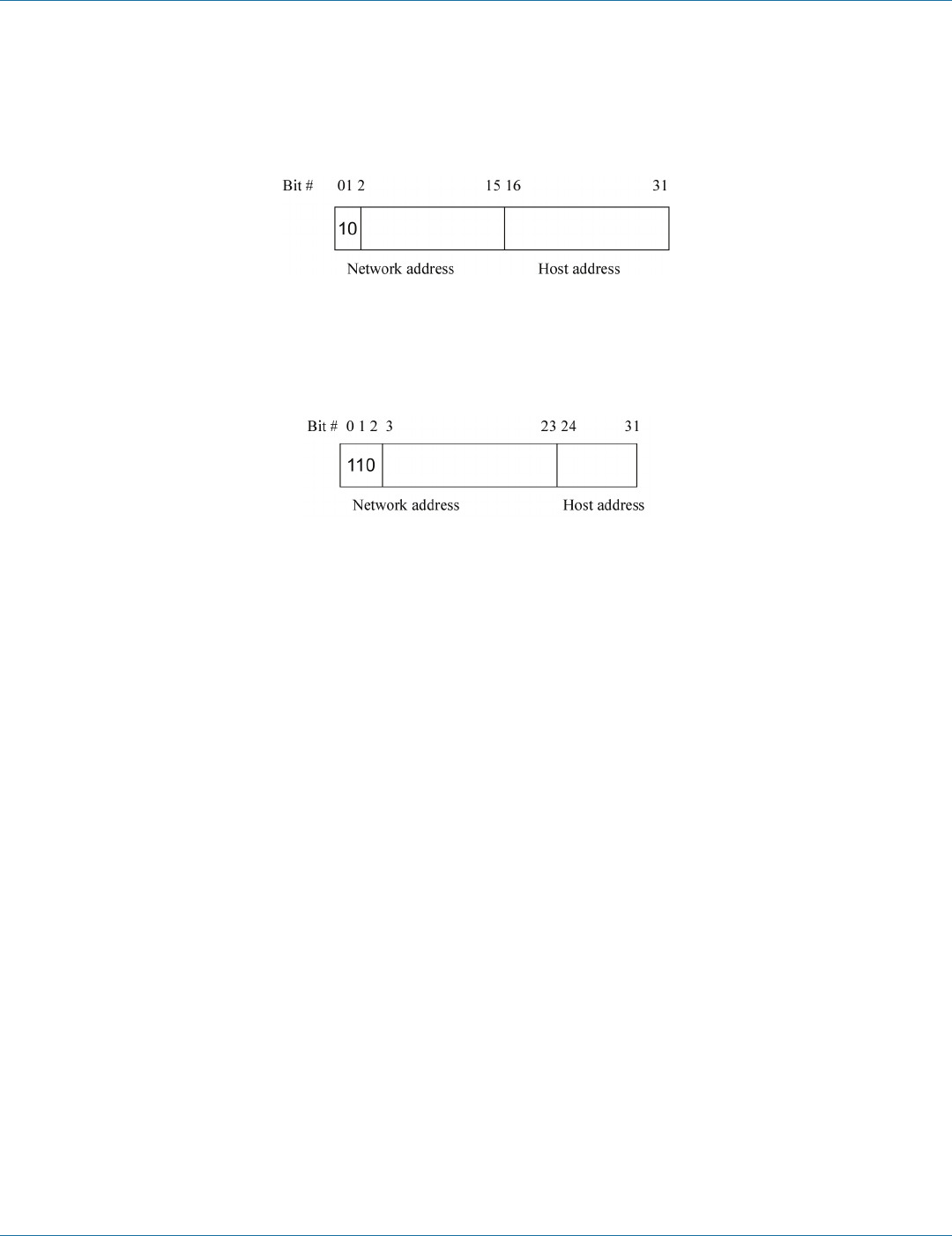
A Class B IP address ranges between 128.0.0.0 and 191.255.255.255. Each class B network has a 16-bit network prefix followed
by a 16-bit host address. There are 16,384 (2
14
)/16 networks able to be defined with a maximum of 65534 (2
16
–2) hosts per
network.
Figure 3-10. Class B IP address.
Class C:
A Class C IP address ranges between 192.0.0.0 and 223.255.255.255. Each class C network has a 24-bit network prefix followed
by an 8-bit host address. There are 2,097,152 (2
21
)/24 networks able to be defined with a maximum of 254 (2
8
–2) hosts per
network.
Figure 3-11. Class C IP address.
Class D and E:
Class D is a class with first 4 MSB (most significant bit) set to 1-1-1-0 and is used for IP multicast. See also RFC 1112.
Class E is a class with first 4 MSB set to 1-1-1-1 and is used for IP broadcast.
According to the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), there are three specific IP address blocks reserved that can be
used for extending an internal network. We call it a private IP address (described below):
Class A 10.0.0.0 --- 10.255.255.255
Class B 172.16.0.0 --- 172.31.255.255
Class C 192.168.0.0 --- 192.168.255.255
Please refer to RFC 1597 and RFC 1466 for more information.
Subnet mask:
A subnet mask is the sub-division of a class-based network or a CIDR block. The subnet is used to determine how to split an IP
address in the network prefix and the host address is based on bits. It uses IP addresses more efficiently and makes it easy to
manage an IP network.
For a class B network, 128.1.2.3, the default subnet mask may be 255.255.0.0, with the first two bytes all 1s. This means more
than 60,000 nodes with a flat IP address will be in the same network. It’s too large to manage practically. If we divide it into
smaller networks by extending the network prefix from 16 bits to, say 24 bits, the switch uses its third byte to subnet this class B
network. The subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, in which each bit of the first three bytes is 1. The first two bytes identify the class B
network, the third byte identifies the subnet within this class B network, and the last byte is the host number.
Not all IP addresses are available in the subnetted network. Two special addresses are reserved. They are the addresses that have
the host number as all zeros and all ones. For example, for an IP address 128.1.2.128, the reserved IP will have all 0s for the
network itself, and all 1s for IP broadcast.