— 29 —
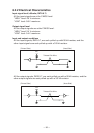
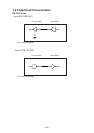
CAUTION:
• The first letter “n” of each signal name indicates that the signal is active “L”.
• If any one of the above signals is not available, bidirectional communication cannot be
accomplished.
• In interfacing signals, be sure to use twist-paired wires for signal lines, and the return
side must be connected to signal ground level.
• All interfacing conditions are specified based on C-MOS level and must satisfy the
following characteristics. Also, specify the rising and falling time of each signal as 0.5
µs.
• Avoid transferring data by ignoring nAck or Busy signal; otherwise, the data may be
erased.
• Make the interface cables as short as necessary.
6.2 Description of Input and Output Signals
6.2.1 Input and Output Signals
Input signals to the printer
• DATA: An 8-bit parallel signal. (Active “High”)
• nStrobe: A strobe signal to help read 8-bit data. (Active “Low”)
• nInit: A signal to reset the entire printer functions. (Active “Low”)
• nSelectIn: This signal is made “High” when the printer is changed to IEEE
1284 mode.
Output signals from the printer
• nAck: An 8-bit data request signal, which is output at the end of a Busy
signal. (Active “Low”)
• Busy: A signal to indicate a busy state of the printer. Input new data
when this signal is “Low”. (Active “High”)
• nFault: This signal becomes “Low” when alarmed. At this time, all control
circuits in the printer are deactivated. (Active “Low”)
• PEerror: A signal to indicate that the paper supply has become low or has
run out completely. (Active “High”)
• DK_STATUS: This signal becomes “High” when the switch is open, and “Low”
when it is closed.
Power related signal
• +5 V: A 5 V signal, which is pulled up by a 3.3 KΩ resistor.
• GND: Common ground on circuits.