200 Managing a Switch Stack
NSF and VoIP
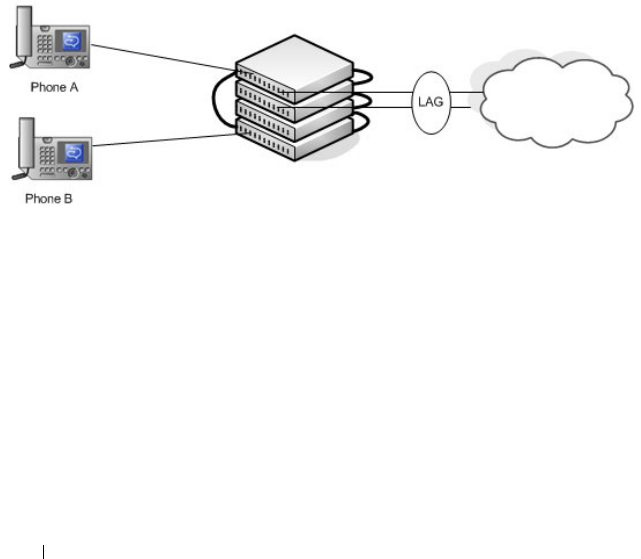
Figure 9-13 shows how NSF maintains existing voice calls during a stack
master failure. Assume the top unit is the stack master. When the stack
master fails, the call from phone A is immediately disconnected. The call
from phone B continues. On the uplink, the forwarding plane removes the
failed LAG member and continues using the remaining LAG member. If
phone B has learned VLAN or priority parameters through LLDP-MED, it
continues to use those parameters. The stack resumes sending LLDPDUs
with MED TLVs once the control plane restarts. Phone B may miss an
LLDPDU from the stack, but should not miss enough PDUs to revert its
VLAN or priority, assuming the administrator has not reduced the LLDPDU
interval or hold count. If phone B is receiving quality of service from policies
installed in the hardware, those policies are retained across the stack master
restart.
Figure 9-13. NSF and VoIP


















