Logical Blocks
A logical block contains user data that is transferred from the host to
the tape drive. Logical blocks can have fixed or variable lengths,
which can be intermixed on the tape. The tape drive supports
uncompressed logical block sizes from 1 to 240 KBytes.
For information about setting the logical block size, refer to the
EXB-8205 and EXB-8505 SCSI Reference.
Logical Block Compression
When writing data in 8500c and 8200c formats, the tape drive
compresses logical blocks of user data before placing them in the
physical blocks. Thus, each physical block contains a compressed
representation of the original user data. Assuming that the
compression algorithm allows user data to be compressed an average
of two times, each physical block written by the tape drive in
compressed format can contain, on average, the compressed
equivalent of 2,048 bytes of user data.
Note: The actual compression ratio achieved by the tape drive in
8500c and 8200c formats depends on the type of data to be
compressed.
For more information about compression, refer to Chapter 3.
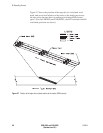
Logical Block Packing
To optimize tape capacity when writing tapes in 8200c, 8500, or 8500c
formats, the tape drive packs logical blocks of user data into physical
blocks. Each 1,024-byte physical block on tape can contain multiple
logical blocks (for example, two 512-byte uncompressed logical blocks
can be written in one physical block). To prevent losing data capacity
when small logical block sizes are used, the tape drive can begin
writing a logical block in one physical block and end in a subsequent
physical block.
Note: In 8200 format, logical blocks are not packed. Only one or
part of one logical block can be written in each physical block.
Figure 2-9 shows three examples of how logical blocks can be written
into one 1,024-byte physical block.
May 1994 EXB-8205 and EXB-8505 2-13
(Standard and XL)
2 Recording Format