URL encoding
URL (Universal Resource Locator) encoding is the method of using ASCII hexadecimal
characters to display specific characters in a URL. It is used for several reasons. On some
operating systems, certain characters are unsafe or not available, and others are reserved by
the HTML or URL specification. URL encoding is used to insure compatibility and functionality
with most Internet browsers. As a general rule, use the hexadecimal encoding method
shown below when these characters appear in your URLs.
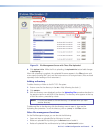
The following types of characters do not require encoding in a URL:
Alphanumeric characters
0-9, a-z, A-Z
Special characters
$ _ - . + ! * ( ) ,
Reserved characters
; / ? : @ = &
NOTE: When used for their reserved purposes, these
characters do not require encoding within a URL.
Figure 37. Characters that Do Not Require Encoding
Reserved characters
Reserved characters should not be encoded when they appear in their conventional meaning
in a URL. For example, do not encode the slash (/) when using it as part of the URL syntax.
Only encode unsafe characters (defined in the table in the next section) in your URLs.
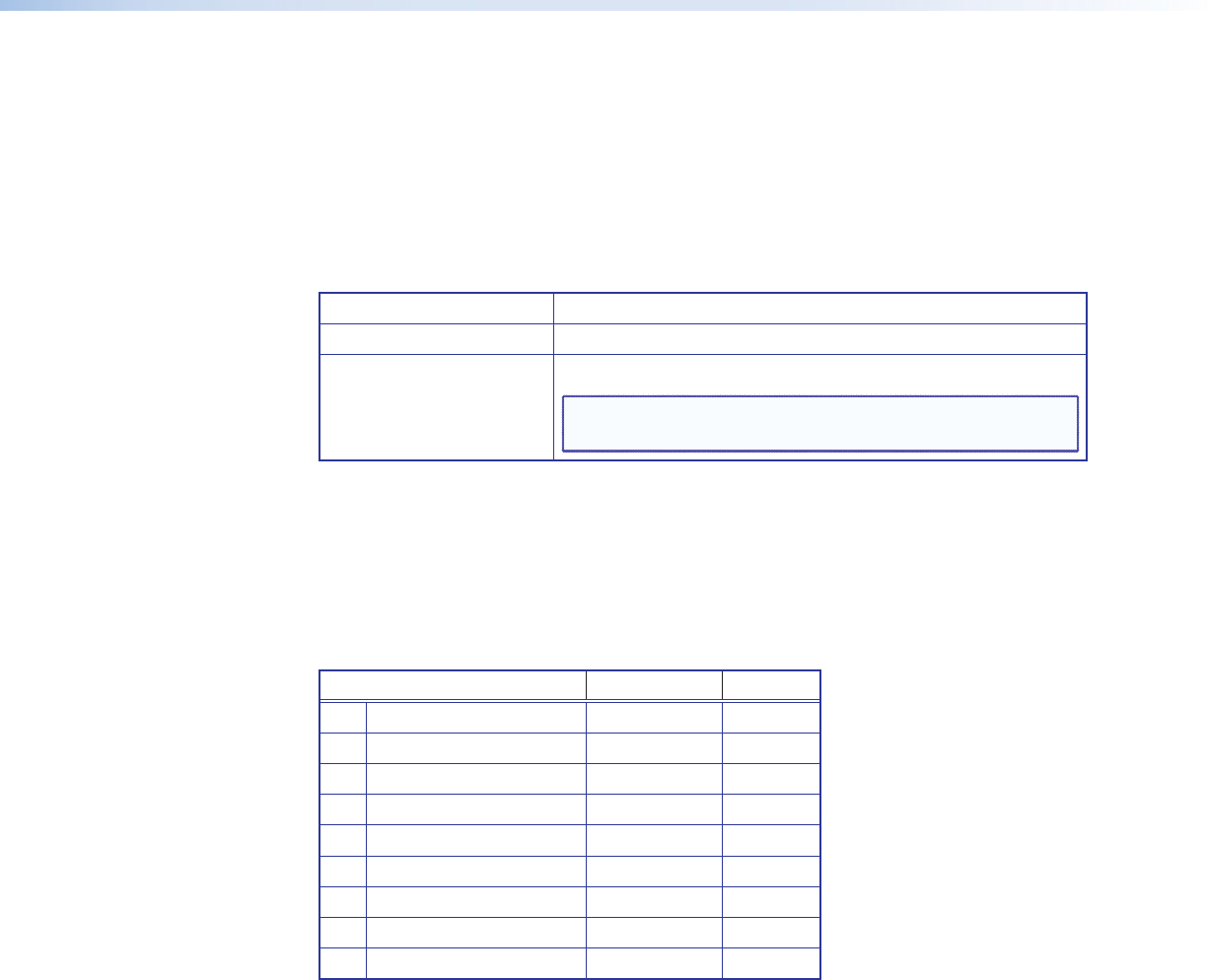
The following table lists reserved characters.
Character Hexadecimal Decimal
$
Dollar
24 36
&
Ampersand
26 38
+
Plus
2B 43
,
Comma
2C 44
/
Forward slash or virgule
2F 47
:
Colon
3B 59
=
Equal
3D 61
?
Question mark
3F 63
@
“At” symbol
40 64
IPL T PC1 • HTML Configuration and Control 42