E-6 More about Integration
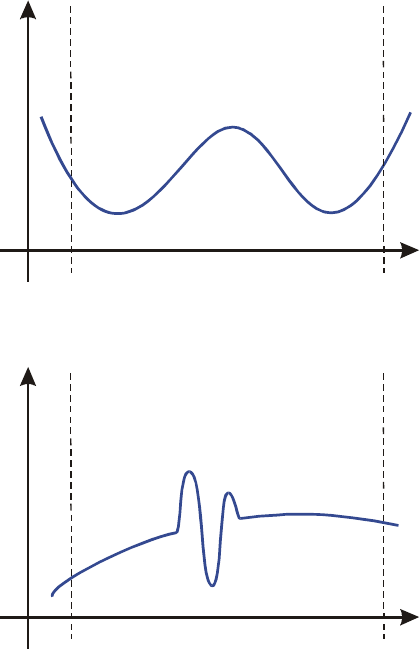
Note that the rapidity of variation in the function (or its low–order derivatives) must
be determined with respect to the width of the interval of integration. With a given
number of sample points, a function f(x) that has three fluctuations can be better
characterized by its samples when these variations are spread out over most of the
interval of integration than if they are confined to only a small fraction of the
interval. (These two situations are shown in the following two illustrations.)
Considering the variations or fluctuation as a type of oscillation in the function, the
criterion of interest is the ratio of the period of the oscillations to the width of the
interval of integration: the larger this ratio, the more quickly the calculation will
finish, and the more reliable will be the resulting approximation.
f (x)
x
Calculated integral
of this function
will be accurate.
f (x)
a b
x
Calculated integral
of this function
may be inaccurate.
a b


















