Page 11-4
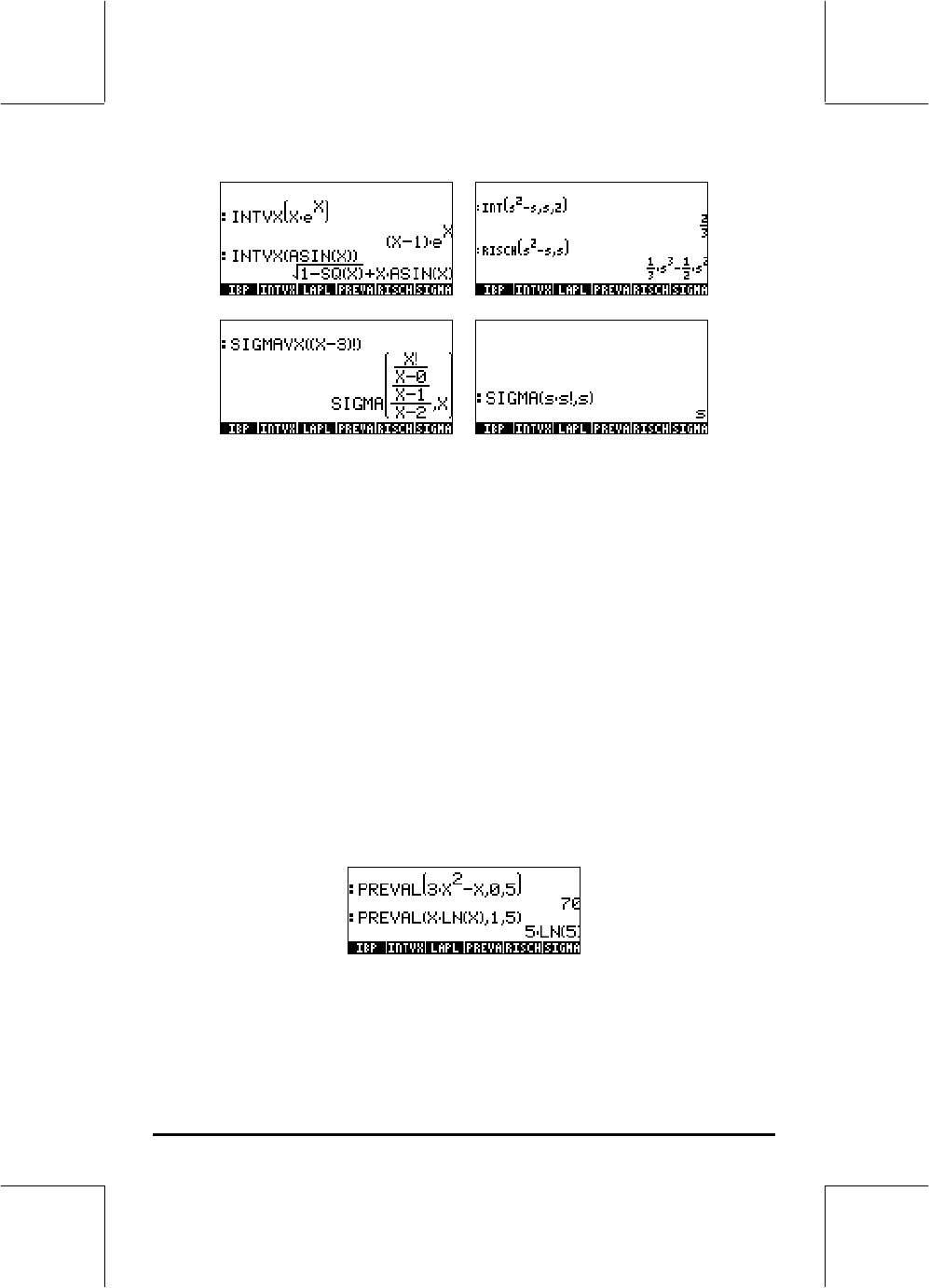
Please notice that functions SIGMAVX and SIGMA are designed for
integrands that involve some sort of integer function like the factorial (!)
function shown above. Their result is the so-called discrete derivative, i.e.,
one defined for integer numbers only.
Definite integrals
In a definite integral of a function, the resulting anti-derivative is evaluated at
the upper and lower limit of an interval (a,b) and the evaluated values
subtracted. Symbolically, we write
),()()( aFbFdxxf
b
a
−=
∫
where f(x) = dF/dx.
To calculate definite integrals of functions using the CAS variable VX (typically,
‘X’), use function PREVAL(f(x),a,b). For example,


















