Page 2-4
This expression is semi-symbolic in the sense that there are floating-point
components to the result, as well as a √3. Next, we switch stack locations
and evaluate using function
Æ
NUM:
™…ï
.
This latter result is purely numerical, so that the two results in the stack,
although representing the same expression, seem different. To verify that they
are not, we subtract the two values and evaluate this difference using function
EVAL: -µ. The result is zero (0.).
For additional information on editing arithmetic expressions in the display or
stack, see Chapter 2 in the calculator’s user's guide.
Creating algebraic expressions
Algebraic expressions include not only numbers, but also variable names. As
an example, we will enter the following algebraic expression:
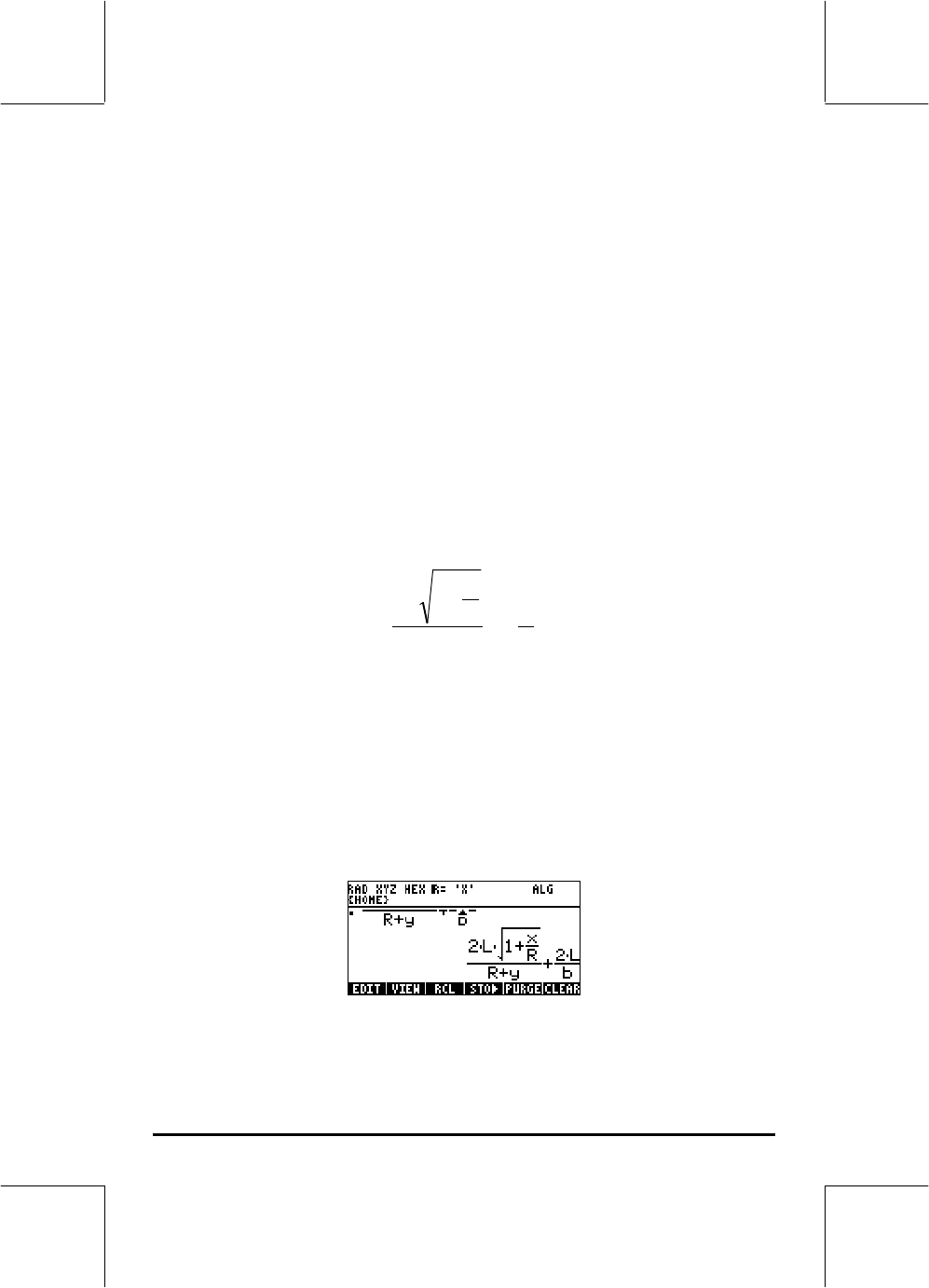
b
L
yR
R
x
L
2
12
+
+
+
We set the calculator operating mode to Algebraic, the CAS to Exact, and the
display to Textbook. To enter this algebraic expression we use the following
keystrokes:
2*~l*R„Ü1+~„x/~r™/„
Ü ~r+~„y™+2*~l/~„b
Press
`
to get the following result: