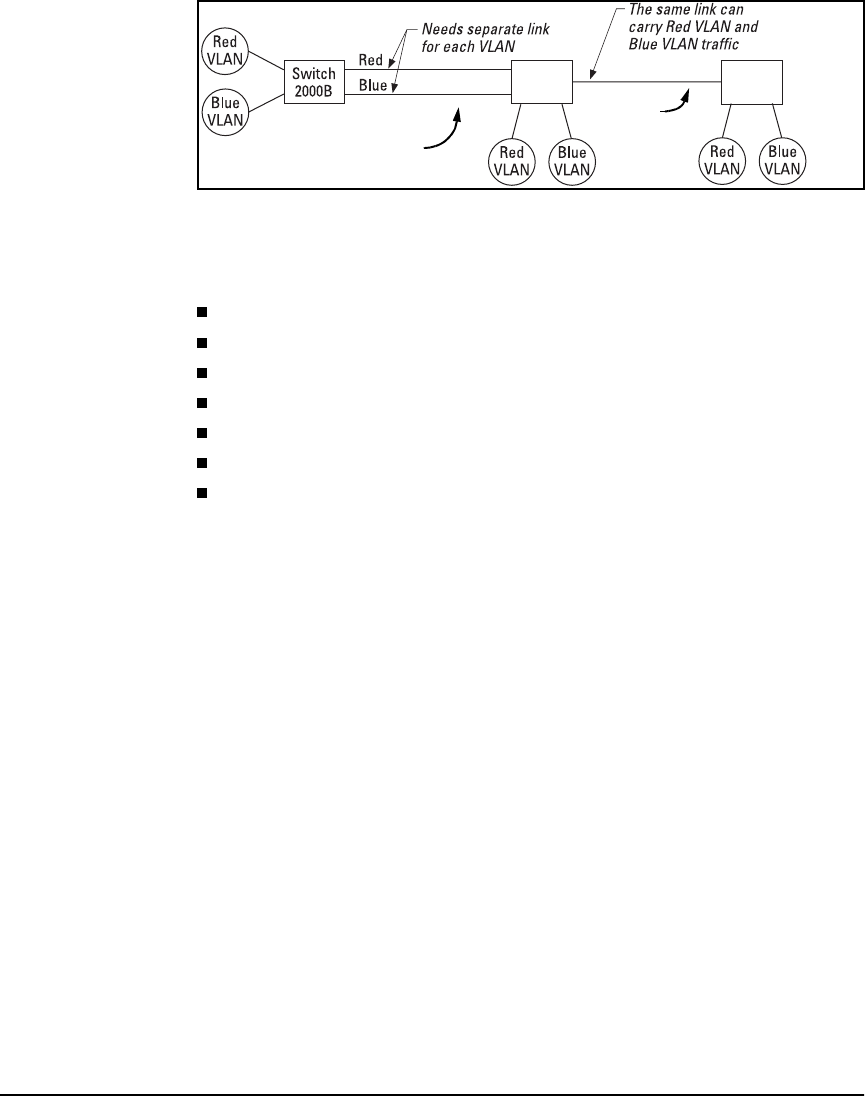
Port-Based Virtual LANs (VLANs) and GVRP
Port-Based Virtual LANs (Static VLANs)
HP
Procurve
Switch
HP
Procurve
Switch
Untagged VLAN Links
Tagged VLAN Link
Figure 11-4. Example of Tagged and Untagged VLAN Technology in the Same
Network
For more information on VLANs, refer to:
“Overview of Using VLANs” (page 11-6)
“Menu: Configuring VLAN Parameters (page 11-10)
“CLI: Configuring VLAN Parameters” (page 11-10)
“Web: Viewing and Configuring VLAN Parameters” (page 11-21)
“VLAN Tagging Information” (page 11-22)
“Effect of VLANs on Other Switch Features” (page 11-31)
“VLAN Restrictions” (page 11-32)
Overview of Using VLANs
VLAN Support and the Default VLAN
In the factory default configuration, VLAN support is enabled and all ports on
the switch belong to the default VLAN (named DEFAULT_VLAN). This places
all ports in the switch into one physical broadcast domain. In the factory-
default state, the default VLAN is the primary VLAN.
You can partition the switch into multiple virtual broadcast domains by adding
one or more additional VLANs and moving ports from the default VLAN to the
new VLANs. (The switch supports up to 256 VLANs.) You can change the name
of the default VLAN, but you cannot change the default VLAN’s VID (which is
always “1”). Although you can remove all ports from the default VLAN, this
VLAN is always present; that is, you cannot delete it from the switch.
The Primary VLAN
Because certain features and management functions run on only one VLAN in
the switch, and because DHCP and Bootp can run per-VLAN, there is a need
for a dedicated VLAN to manage these features and ensure that multiple
instances of DHCP or Bootp on different VLANs do not result in conflicting
11-6


















