PX875P PRO/ PX875P
14
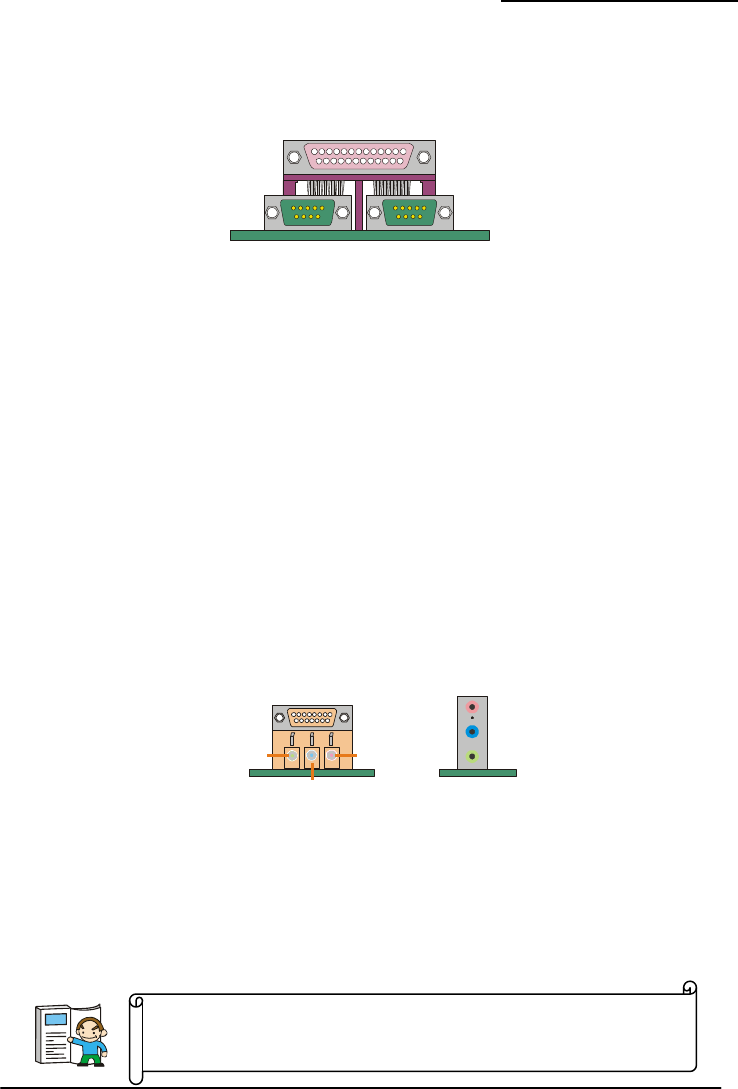
Serial and Parallel Interface Ports
The series mainboard comes equipped with two serial ports
and one parallel port on the back panel.
These interface ports will be explained below.
llel interface.
The Serial Interface: COM1/ COM2
The serial interface port is some r ronous
communication port. Mice, modems and other perip can con port.
Game Port Connector (only 875 PR
This connector allows you to connect a joystick or game pad for playing computer games. This port
can also be used to connect to MIDI devices.
wo speakers each.
peaker-Out Connects to standard audio speake eadphon port becomes the front
eakers when 5.1 Channel Audio Effe iver is in d and enabled.
ine In Connects to devices
at provide audio input. This port becomes the rear speakers when 5.1 Channel Audio Effects driver
i enabled.
n Connects to a microphone. This port becomes oofer/center out when 5.1 nel
udio Effects driver is installed and
Parallel Interface Port: PRT
The parallel port on your system has a 25-pin, DB25 connector and is used to interface with parallel
printers and other devices using a para
times eferred to as an RS-232 port or an asynch
heral devices be nected to a serial
for PX P O V1.0)
Audio Port Connectors
This mainboard comes equipped with three Audio Ports. The three ports, Mic-in, Line-in and
Speaker-out are standard audio ports that provides basic audio functionality. After you install the 5.1
Channel drivers and setup 5.1 channel Audio effect, the three audio ports are enabled for 5.1 channel
and supporting t
S rs or h es. This
sp cts dr stalle
L
th
an external audio device such as a CD player, tape player or other audio
is nstalled and
Mic I
A
the subw Chan
enabled.
Printer Port
COM1 COM2
This mainboard supports Super 5.1 Channel Audio effects which turns
your standard Speaker Out, Lin In, Mic In audio connectors into a 6
channel audio system. See Appendix II for more information.
Speaker
Line In
O
Mic In
ut
Speaker Out
Game Port
In
Mic In
Line
( 1.0) (For V2For V .0)


















